Market Intelligence
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Intelligence
In today's highly competitive business landscape, staying ahead of the curve is essential for success. Market intelligence, the art and science of gathering, analyzing, and applying relevant data, plays a pivotal role in strategic decision-making. In this chapter, we'll define market intelligence and explore why it's crucial for businesses of all sizes.
Chapter 2: The Components of Market Intelligence
Market intelligence encompasses a wide range of activities and data sources. In this chapter, we'll break down the key components of market intelligence, including competitive analysis, customer insights, industry trends, and more. Understanding these components is the foundation for building effective market intelligence strategies.
Chapter 3: The Importance of Data in Market Intelligence
Data is the lifeblood of market intelligence. This chapter delves into the significance of data in the market intelligence process. From primary and secondary data sources to big data analytics, we'll explore the various data types and how they contribute to informed decision-making.
Chapter 4: Gathering Market Intelligence
This chapter provides insights into the methods and techniques used to collect valuable market intelligence. We'll discuss surveys, interviews, focus groups, social media monitoring, and other data collection strategies, highlighting their advantages and limitations.
Chapter 5: Analyzing Market Intelligence
Once data is collected, the next crucial step is analysis. In this chapter, we'll dive deep into data analysis methods, such as SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter's Five Forces, to uncover actionable insights from your market intelligence.
Chapter 6: Competitive Intelligence
A core aspect of market intelligence is understanding your competitors. This chapter explores the world of competitive intelligence, detailing how to identify competitors, track their strategies, and use this information to gain a competitive edge.
Chapter 7: Customer-Centric Market Intelligence
Customers are at the heart of every successful business. Learn how to gather and utilize customer insights to refine your products, services, and marketing strategies. We'll also discuss customer segmentation and persona development.
Chapter 8: Industry Trends and Market Forecasting
Staying up-to-date with industry trends and predicting future market conditions is vital. In this chapter, we'll explore tools and techniques for monitoring trends, forecasting market changes, and adapting your business accordingly.
Chapter 9: Turning Market Intelligence into Action
Collecting and analyzing market intelligence is just the beginning. In this chapter, we'll discuss how to translate your insights into actionable strategies and tactics. From product development to marketing campaigns, you'll learn how to apply market intelligence effectively.
Chapter 10: Challenges and Future of Market Intelligence
As the business landscape evolves, so does market intelligence. In this final chapter, we'll examine the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for market intelligence. We'll also explore emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning and their impact on the future of market intelligence.
Conclusion: Market intelligence is not just a buzzword; it's a critical tool for businesses seeking sustainable growth and success. This comprehensive guide has taken you through the fundamentals of market intelligence, from its components and data-driven approach to its application in competitive analysis, customer-centric strategies, and more. Armed with this knowledge, you can harness the power of market intelligence to make informed decisions and stay ahead in today's dynamic business environment.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Intelligence
Chapter 2: The Components of Market Intelligence
Chapter 3: The Importance of Data in Market Intelligence
Chapter 4: Gathering Market Intelligence
Chapter 5: Analyzing Market Intelligence
Chapter 6: Competitive Intelligence
Chapter 7: Customer-Centric Market Intelligence
Chapter 8: Industry Trends and Market Forecasting
Chapter 9: Turning Market Intelligence into Action
Chapter 10: Challenges and the Future of Market Intelligence
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Intelligence
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, globalization, and fierce competition, businesses face a constant challenge to navigate the ever-changing marketplace successfully. To thrive in such an environment, companies need to make informed decisions, anticipate trends, and outmaneuver competitors. This is where a market intelligence platform steps in as an indispensable strategic tool.
Market Intelligence, often referred to as MI, is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data and information to gain a deep understanding of the market and its dynamics. It enables organizations to make well-informed decisions, minimize risks, and identify growth opportunities. In this introductory exploration of Market Intelligence, we'll delve into its fundamental concepts, significance, and how it can be harnessed to drive business success.
The Essence of Market Intelligence
At its core, Market Intelligence is about acquiring knowledge – knowledge about your industry, your competitors, your customers, and your own business. It involves the systematic gathering and interpretation of data from various sources, both internal and external, to create a holistic picture of the market landscape.
Why Market Intelligence Matters
- Informed Decision-Making: One of the primary reasons businesses invest in Market Intelligence is to make informed decisions. By having access to accurate, up-to-date information about market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes, companies can make strategic choices that are more likely to lead to success.
- Competitive Advantage: In today's cutthroat business environment, staying ahead of the competition is crucial. MI allows companies to understand what their competitors are doing, identify gaps in the market, and develop strategies to gain a competitive edge.
- Risk Mitigation: Business decisions inherently carry risks. MI helps in risk assessment by providing insights into potential challenges and threats. Armed with this knowledge, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate risks effectively.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Successful businesses are those that meet the needs and desires of their customers. MI aids in understanding customer behavior, preferences, and pain points, enabling companies to tailor their products and services accordingly.
- Strategic Planning: Market Intelligence plays a pivotal role in strategic planning. It helps organizations set achievable goals, allocate resources effectively, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Key Components of Market Intelligence
Market Intelligence is a multifaceted discipline that involves several key components:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including industry research, customer feedback, competitor analysis, and internal metrics.
- Data Analysis: Processing and interpreting data to extract meaningful insights. This often involves statistical analysis, trend analysis, and data visualization.
- Competitive Intelligence: Focusing on understanding and analyzing competitors' strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Customer Intelligence: Delving into customer demographics, behaviors, and feedback to better cater to their needs.
- Market Research: Conducting in-depth studies and surveys to gain a deep understanding of market trends, customer sentiment, and industry developments.
- Technology and Tools: Leveraging technological solutions, such as data analytics software and business intelligence platforms, to streamline the MI process.
Conclusion
Market Intelligence is not just a buzzword but a strategic imperative in today's business landscape. It equips organizations with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate the complexities of the market, make informed decisions, and stay ahead of the competition. In the chapters to come, we will explore the intricacies of Market Intelligence in greater detail, including data collection methods, analysis techniques, and real-world applications. Stay tuned to unlock the full potential of Market Intelligence and propel your business toward success.
Chapter 2: The Components of Market Intelligence
Market Intelligence (MI) is a multifaceted discipline that involves a comprehensive understanding of various components. These components work in harmony to provide businesses with valuable insights into the market landscape. In this chapter, we will delve into the key components of Market Intelligence, each playing a vital role in helping organizations make informed decisions and stay competitive.
- Competitive Intelligence (CI): Competitive Intelligence focuses on gathering and analyzing information about your competitors. This component helps you understand your competition's strategies, strengths, weaknesses, product offerings, pricing, and market positioning. By keeping a close eye on your rivals, you can identify opportunities to differentiate your products or services and gain a competitive advantage.
- Customer Intelligence: Customer Intelligence is all about understanding your customers. It involves collecting data on customer preferences, behaviors, demographics, and feedback. This component helps you create buyer personas, tailor marketing strategies, enhance customer experiences, and develop products or services that resonate with your target audience.
- New Market Research: Market Research is a systematic process of collecting and analyzing data about the market, including its size, trends, growth potential, and consumer behavior. This component provides a solid foundation for decision-making by offering insights into market dynamics, customer needs, and potential opportunities or threats.
- Industry Analysis: Industry Analysis involves studying the broader industry in which your business operates. It includes monitoring industry trends, regulatory changes, emerging technologies, and macroeconomic factors that can impact your business. A comprehensive industry analysis helps you adapt to changing market conditions and stay ahead of industry shifts.
- Product and Service Analysis: This component involves an in-depth assessment of your own products or services. By analyzing product performance, customer feedback, and market demand, you can identify areas for improvement, refine your offerings, and develop new features or products that align with market needs.
- Technology and Tools: In today's data-driven world, technology plays a crucial role in Market Intelligence. Advanced tools and platforms, such as data analytics software, business intelligence dashboards, and artificial intelligence, help automate data collection, analysis, and reporting processes, making MI more efficient and accurate.
- Market Segmentation: Segmentation involves dividing your target market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, such as age, gender, location, or buying behavior. This component allows you to tailor your marketing strategies to specific segments, addressing their unique needs and preferences.
- Risk Analysis: Market Intelligence also includes assessing potential risks and challenges that may affect your business. By identifying risks early on, you can develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate them, ensuring the continuity of your operations.
- Regulatory and Compliance Analysis: Understanding and staying compliant with industry regulations and legal requirements is essential. Market Intelligence encompasses the monitoring of regulatory changes and compliance issues that may impact your business operations.
- Data Sources: Effective MI relies on a diverse range of data sources, both internal and external. Internal data may include sales records, customer databases, and product performance metrics, while external sources may comprise industry reports, market surveys, social media data, and competitor websites.
In the subsequent chapters, we will delve deeper into each of these components, exploring strategies and techniques for effective data collection, analysis, and utilization. A well-rounded understanding of these MI components is crucial for businesses seeking to harness the power of information to make strategic decisions and drive growth.
Chapter 3: The Importance of Data in Market Intelligence
In the world of Market Intelligence (MI), data is the cornerstone upon which informed decision-making is built. Without robust data, the process of gathering insights, understanding market dynamics, and staying competitive becomes challenging if not impossible. In this chapter, we'll explore the critical role of data in MI and why it's indispensable for businesses seeking to thrive in today's complex marketplace.
- Data as the Foundation of MI: Data is the raw material from which MI derives its value. It provides the necessary information to understand market trends, customer preferences, competitor activities, and industry developments. Without data, MI would lack the substance needed to make informed decisions.
- Primary vs. Secondary Data: Data in MI can be categorized as primary or secondary. Primary data is collected directly from original sources, such as surveys, interviews, and customer feedback. Secondary data, on the other hand, is pre-existing information gathered by external sources, such as market research reports, industry publications, and government statistics. Both types of data are crucial in building a comprehensive picture of the market.
- Big Data and Advanced Analytics: In the era of big data, businesses have access to vast amounts of information. MI leverages advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and data mining, to sift through this data deluge and extract meaningful insights. These insights can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional analysis.
- Real-Time Data: The speed at which data is generated and processed has increased exponentially. Real-time data feeds from sources like social media, IoT devices, and online sales platforms enable businesses to react swiftly to market changes and customer feedback. This agility is a competitive advantage in today's fast-paced business environment.
- Customer-Centric Insights: Data allows businesses to gain a deep understanding of their customers. Through data analysis, companies can segment their customer base, track customer behaviors, and identify preferences and pain points. This customer-centric approach enables businesses to tailor their products, services, and marketing strategies effectively.
- Competitive Analysis: Data is equally vital for competitive analysis in MI. By collecting data on competitors' pricing, product launches, marketing campaigns, and customer reviews, organizations can develop strategies to outmaneuver rivals and gain a competitive edge.
- Risk Assessment: MI relies on data to assess potential risks and challenges. By analyzing historical data and monitoring market indicators, businesses can identify emerging risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
- Trend Identification: Data-driven MI allows organizations to spot trends and market shifts early on. Whether it's a change in consumer behavior, emerging technologies, or shifts in industry regulations, data can act as an early warning system, helping businesses adapt and stay ahead of the curve.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Incorporating data into decision-making processes enhances the accuracy and objectivity of choices. Businesses can rely on data-backed insights to allocate resources, develop new products, optimize pricing strategies, and expand into new markets with greater confidence.
- Continuous Improvement: Data is not static; it evolves over time. MI involves a continuous process of data collection, analysis, and adaptation. This iterative approach allows businesses to fine-tune their strategies and remain relevant and competitive.
In the following chapters, we will explore the various methods and techniques for gathering, analyzing, and leveraging data effectively in the MI process. Understanding the importance of data and how it forms the bedrock of Market Intelligence is essential for businesses striving to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of today's marketplace.
Chapter 4: Gathering Market Intelligence
Effective Market Intelligence (MI) begins with the collection of relevant and reliable data from various sources. The process of gathering MI is crucial because the quality and comprehensiveness of the data directly impact the insights and decisions that can be derived from it. In this chapter, we'll delve into the methods and techniques used for gathering market intelligence.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires are a direct way to gather information from your target audience. They can be conducted online, over the phone, or in person. Structured surveys help in collecting quantitative data, while open-ended questions can yield qualitative insights. Surveys and questionnaires are useful for understanding customer preferences, satisfaction levels, and feedback.
- Interviews: Interviews, whether one-on-one or group, allow for in-depth conversations with individuals or representatives of your target market. They are particularly valuable for gathering qualitative data and uncovering nuanced insights. Interviews can be semi-structured or unstructured, depending on the research goals.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups involve bringing together a small, diverse group of individuals to discuss specific topics or products. These sessions are moderated and provide qualitative insights into consumer opinions, attitudes, and perceptions. Focus groups are valuable for product development, marketing campaign testing, and idea generation.
- Online Research: The internet is a treasure trove of information. Online research involves scouring websites, forums, social media platforms, and online reviews to gather data on consumer sentiment, competitor activities, and industry trends. Automated web scraping tools can aid in collecting large volumes of data efficiently.
- Social Media Monitoring: Social media platforms are rich sources of real-time data. Monitoring social media conversations, mentions, and hashtags related to your industry or brand can provide insights into customer sentiment, emerging trends, and potential issues. Various social media listening tools are available to automate this process.
- Competitor Analysis: Studying your competitors is a fundamental part of MI. This involves analyzing their websites, product offerings, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, and customer reviews. Competitive intelligence tools and services can help gather and organize competitor data.
- Industry Reports and Publications: Industry-specific reports, whitepapers, and publications from reputable sources can offer a wealth of data and insights about market trends, forecasts, and key players. These reports often contain statistical data and expert analyses.
- Government and Regulatory Data: Government agencies frequently provide valuable data, including economic indicators, demographic statistics, and industry-specific reports. Accessing and analyzing government data can provide a broader context for market intelligence efforts.
- Trade Shows and Conferences: Attending industry-specific trade shows and conferences allows you to gather MI by networking with industry experts, observing new product launches, and participating in seminars and workshops. It's an excellent way to stay updated on the latest developments and innovations.
- Customer Feedback and Surveys: Listening to your existing customers is essential. Collect feedback through customer surveys, online reviews, and customer service interactions. Analyzing this data can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your offerings.
- Expert Interviews: In addition to customer interviews, conducting interviews with industry experts, thought leaders, and influencers can provide valuable insights into market trends and emerging technologies.
- Supplier and Distributor Insights: Suppliers and distributors often have a unique perspective on the market. Gathering insights from them can help you understand supply chain dynamics, pricing trends, and potential disruptions.
- Internal Data: Don't overlook your internal data sources. Analyzing your own sales data, customer databases, and performance metrics can yield valuable insights into your own business and customer behavior.
- Mystery Shopping: Mystery shopping involves sending undercover shoppers to assess the quality of your products or services and those of your competitors. This technique can help you gain firsthand insights into customer experiences.
- Trade Associations: Industry-specific trade associations often provide valuable market data, industry benchmarks, and networking opportunities.
Successful MI relies on a combination of these data collection methods, tailored to your specific research objectives. It's crucial to ensure that data is collected ethically, securely, and in compliance with privacy regulations. In the next chapters, we'll explore how to analyze and make sense of the data gathered through these methods to derive actionable insights for your business.
Chapter 5: Analyzing Market Intelligence
Collecting data is just the first step in the Market Intelligence (MI) process. To derive actionable insights and make informed decisions, you must effectively analyze the data you've gathered. In this chapter, we'll explore various methods and techniques for analyzing market intelligence.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a widely-used framework for assessing the internal and external factors that affect a business. It helps identify areas of strength and weakness within your organization and opportunities and threats in the market. SWOT analysis is particularly useful for strategic planning.
- PESTEL Analysis: PESTEL analysis examines the macro-environmental factors that can impact a business: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal. This comprehensive analysis helps businesses understand the broader context in which they operate and anticipate potential changes or challenges.
- Porter's Five Forces Analysis: Porter's Five Forces is a framework that assesses the competitive forces within an industry. It examines the bargaining power of suppliers, buyers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. This analysis helps in determining the attractiveness of an industry.
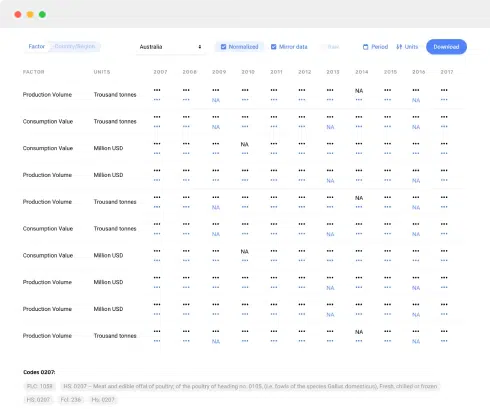
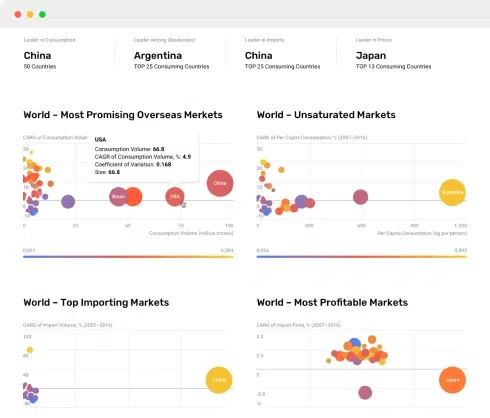
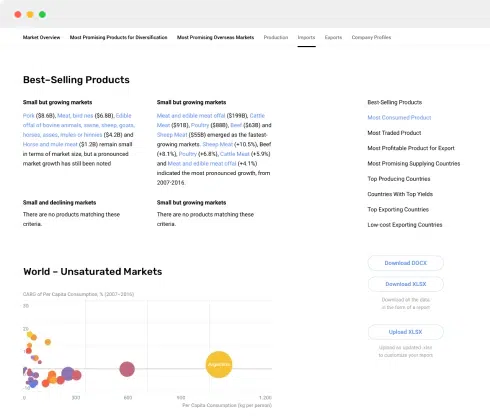
- Data Visualization: Data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards, are essential for making complex data more understandable and actionable. Visualization tools help in spotting trends, patterns, and outliers quickly.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical techniques, such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and correlation analysis, are used to identify relationships and trends within data sets. These methods can provide quantitative insights into factors that affect your business.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing your performance and metrics with those of competitors or industry leaders. It helps identify areas where your business may lag behind or excel, allowing you to set improvement goals.
- Customer Segmentation: Segmenting your customer base based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences can reveal distinct customer groups with unique needs. This analysis enables targeted marketing and product/service customization.
- Market Trends Analysis: Monitoring and analyzing market trends over time allows businesses to anticipate changes in consumer behavior and preferences. Recognizing emerging trends early can give you a competitive advantage.
- Sentiment Analysis: Sentiment analysis uses natural language processing and machine learning to assess the sentiment expressed in customer reviews, social media posts, and other textual data. It helps gauge customer opinions and reactions to products, services, and marketing campaigns.
- Competitive Intelligence Analysis: Analyzing data collected on competitors can reveal insights into their strategies, market positioning, and areas where you can outperform them. This analysis is crucial for developing competitive strategies.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: Mining customer feedback, whether through surveys or online reviews, allows you to identify common issues, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. It helps in enhancing customer experiences.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves assessing various "what-if" scenarios to understand the potential outcomes of different strategic decisions. This technique aids in risk assessment and decision-making.
- Trend Extrapolation: Based on historical data and current trends, trend extrapolation involves making predictions about future market conditions. It can guide long-term planning and forecasting.
- Pattern Recognition: Pattern recognition techniques, such as machine learning algorithms, can identify patterns and anomalies within large datasets, helping in predictive analysis and anomaly detection.
- Expert Opinions: Incorporating insights from industry experts, consultants, or internal experts can provide valuable qualitative context to quantitative data analysis.
Effective MI analysis combines quantitative and qualitative methods, leveraging both data-driven insights and expert opinions. The choice of analysis techniques depends on your research objectives and the nature of the data you've collected. In the next chapters, we'll explore how to turn these insights into actionable strategies and tactics for your business.
Chapter 6: Competitive Intelligence
In the dynamic and competitive business landscape, staying ahead of the competition is essential for long-term success. Competitive Intelligence (CI) is the practice of systematically gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about competitors, industry trends, and market dynamics to gain a strategic advantage. In this chapter, we'll explore the significance of CI and the methods employed to gather and leverage competitive intelligence effectively.
Why Competitive Intelligence Matters:
- Strategic Decision-Making: CI equips organizations with insights into their competitors' strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. This information is invaluable for making informed strategic decisions.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding the competitive landscape helps identify potential threats and challenges. By anticipating competitor actions and market shifts, businesses can take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
- Innovation and Product Development: CI can reveal gaps in the market that competitors haven't addressed. This insight can fuel innovation and guide the development of products or services that outperform rivals.
- Pricing Strategies: Analyzing competitor pricing strategies allows businesses to position themselves competitively in the market. It helps in setting optimal pricing for products and services.
- Marketing and Positioning: CI helps in crafting effective marketing campaigns that target weaknesses in competitors' offerings or capitalize on your own strengths. It aids in brand positioning and differentiation.
- Identifying Market Trends: CI provides visibility into industry trends, emerging technologies, and changing customer preferences. This knowledge can guide businesses in aligning their strategies with market dynamics.
Methods for Gathering Competitive Intelligence:
- Competitor Websites: Analyzing competitor websites can reveal information about their products, pricing, customer reviews, and marketing strategies. Regularly monitoring competitors' websites is a fundamental CI practice.
- Market Research Reports: Industry-specific market research reports and studies often provide insights into competitors' market share, growth strategies, and financial performance. These reports are valuable sources of secondary data.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring competitors' social media profiles and activities can unveil their marketing strategies, customer engagement, and public sentiment. It's a real-time source of competitive intelligence.
- Trade Shows and Conferences: Attending industry events can offer opportunities to observe competitors' product launches, marketing efforts, and networking activities. It's also a chance to interact with industry experts and gather insider insights.
- Customer Feedback and Reviews: Analyzing customer feedback, reviews, and ratings of competitors' products or services can provide insights into customer satisfaction, pain points, and areas for improvement.
- Competitor Interviews: In some cases, engaging in competitive interviews (through legitimate channels) with former employees or industry insiders can yield valuable insights into a competitor's operations, strategies, and weaknesses.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance metrics against those of competitors or industry leaders. It helps identify areas where you lag or excel.
- Supplier and Distributor Information: Suppliers and distributors often have insights into competitors' supply chain strategies, pricing negotiations, and product availability. Building strong relationships with these stakeholders can provide a competitive edge.
- Patent and Intellectual Property Analysis: Examining competitors' patents, trademarks, and intellectual property filings can reveal their research and development efforts, innovation focus, and potential future product launches.
- News and Media Monitoring: Keeping an eye on news articles, press releases, and industry publications can uncover information about competitors' recent developments, partnerships, mergers, or acquisitions.
Ethical Considerations: It's essential to conduct competitive intelligence ethically and within the bounds of the law. Unethical practices, such as corporate espionage or data breaches, can lead to legal consequences and damage a company's reputation.
In the following chapters, we'll explore how to analyze and leverage the competitive intelligence gathered to develop effective strategies and tactics that give your business a competitive edge.
Chapter 7: Customer-Centric Market Intelligence
In today's highly competitive business environment, understanding your customers is paramount. Customer-Centric Market Intelligence (CCMI) is the practice of gathering, analyzing, and leveraging data and insights about your customers to enhance their experiences, drive loyalty, and grow your business. In this chapter, we'll delve into the significance of CCMI and explore the methods for effectively collecting and utilizing customer-centric data.
Why Customer-Centric Market Intelligence Matters:
- Improved Customer Experiences: CCMI helps businesses tailor their products, services, and interactions to meet the unique needs and preferences of their customers. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Better Targeting: By segmenting customers based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences, CCMI enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns and personalized offers that resonate with specific customer groups.
- Reduced Churn: Understanding customer feedback and pain points allows businesses to proactively address issues, reducing customer churn and increasing customer retention rates.
- Product Development: Customer feedback and insights guide the development of new products or the improvement of existing ones. This ensures that products align with customer expectations.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that prioritize customer-centricity gain a competitive edge by consistently delivering value and superior experiences. Satisfied customers are more likely to become brand advocates.
Methods for Gathering Customer-Centric Market Intelligence:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires are versatile tools for gathering customer feedback. They can be conducted through email, web forms, or in-app surveys. Questions can be designed to gather insights on satisfaction, preferences, and pain points.
- Customer Interviews: In-depth interviews with customers provide qualitative insights into their experiences, challenges, and expectations. These interviews can uncover valuable feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms for mentions of your brand, products, or industry allows you to gauge customer sentiment and identify emerging trends or issues.
- Online Reviews and Ratings: Analyzing online reviews on platforms like Yelp, Amazon, or Google provides insights into what customers like and dislike about your products or services. Pay attention to both positive and negative feedback.
- Customer Support Data: Data from customer support interactions, such as chat logs and call recordings, can highlight common customer issues and areas where additional support or training may be needed.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Mapping the customer journey helps identify touchpoints where customers interact with your brand. This analysis helps in optimizing these touchpoints for a seamless experience.
- Website Analytics: Analyzing website traffic and user behavior through tools like Google Analytics can reveal which pages are most visited, where users drop off, and what content or products are of interest to customers.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS surveys measure customer loyalty and satisfaction by asking customers how likely they are to recommend your business to others. It's a simple yet effective metric to gauge customer sentiment.
- Customer Segmentation: Segmenting your customer base based on demographics, behaviors, and purchase history allows for targeted marketing and personalized messaging.
- Feedback Forms: Implement feedback forms on your website or within your products/services to gather real-time input from users. These forms can be used to identify issues and areas for improvement.
Utilizing Customer-Centric Insights:
Once you've gathered customer-centric data, it's crucial to use these insights effectively:
- Customer Personas: Develop detailed customer personas based on data and insights. Personas represent typical customer profiles and help in targeting marketing efforts.
- Improvement Initiatives: Act on customer feedback and pain points to continuously improve products, services, and processes.
- Personalized Marketing: Use customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns, recommendations, and offers.
- Customer Training: If customers struggle with your products or services, provide training resources and support to enhance their experience.
- Retention Strategies: Implement customer retention strategies based on data, such as loyalty programs, exclusive offers, or follow-up surveys.
- Predictive Analytics: Use customer data for predictive analytics to forecast future trends and customer behaviors.
Customer-Centric Market Intelligence is an ongoing process that involves listening to your customers, analyzing their feedback, and taking proactive steps to meet their needs. By prioritizing customer-centricity, businesses can build lasting relationships, foster loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth.
Chapter 8: Industry Trends and Market Forecasting
Keeping a finger on the pulse of industry trends and accurately forecasting market developments are essential components of effective Market Intelligence (MI). In this chapter, we will explore why industry trends and market forecasting are crucial and discuss the methods and tools used to stay ahead in a rapidly changing business landscape.
The Significance of Industry Trends and Market Forecasting:
- Strategic Planning: Industry trends and forecasts provide critical inputs for long-term strategic planning. They help businesses align their goals, investments, and resources with expected market shifts.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding industry trends and forecasting potential changes allows companies to proactively address challenges and adapt to evolving market conditions, reducing risks.
- Competitive Advantage: Staying ahead of industry trends gives businesses an advantage over competitors who may be slower to react. It allows for the development of innovative products and services that cater to emerging customer demands.
- Resource Allocation: Accurate market forecasts help in efficient resource allocation. Businesses can optimize production, inventory, and staffing based on anticipated demand.
- Customer-Centricity: Monitoring industry trends helps identify shifts in customer preferences and behavior. This insight guides businesses in tailoring their offerings to meet evolving customer needs.
Methods for Tracking Industry Trends:
- Free market Research Reports: Industry-specific market research reports from reputable sources offer valuable insights into current trends, growth potential, and emerging opportunities.
- Trade Publications: Industry trade publications, journals, and magazines often feature articles and reports on the latest trends and developments within a specific sector.
- Industry Conferences and Events: Attending conferences, seminars, and industry events allows businesses to gain firsthand knowledge of emerging trends, technologies, and best practices.
- Competitor Analysis: Studying competitors can reveal how they are adapting to industry trends, what strategies they are implementing, and where they are investing resources.
- Expert Interviews: Conducting interviews with industry experts, thought leaders, and consultants can provide qualitative insights into the factors driving industry trends.
- Online Trend Analysis Tools: Online tools and platforms, such as Google Trends and social media monitoring tools, allow businesses to track online conversations and interest in specific topics or keywords.
- Customer Feedback and Surveys: Customer feedback can offer insights into emerging trends and changing preferences. Surveys and feedback forms can be used to gather such information.
Methods for Market Forecasting:
- Historical Data Analysis: Examining historical sales data, market trends, and past performance can provide a foundation for forecasting future market conditions.
- Regression Analysis: Regression models analyze the relationship between different variables to predict future outcomes. It's commonly used in forecasting demand based on historical data.
- Time Series Analysis: Time series models examine data points over time to identify patterns and trends, helping in predicting future values.
- Expert Opinions: Expert opinions and industry insights can be valuable for qualitative forecasting, especially in rapidly evolving industries.
- Market Surveys and Research: Conducting market surveys and research studies can provide quantitative data for forecasting consumer preferences, demand, and market size.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves considering multiple future scenarios and their potential impact on your business. This technique helps in contingency planning and risk assessment.
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of data to generate forecasts and predictions. These models can adapt to changing market dynamics.
- Economic Indicators: Monitoring economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment rates, can provide insights into broader market trends and economic conditions.
Utilizing Trend Analysis and Market Forecasting:
Once you've gathered data and made forecasts, it's essential to leverage this information effectively:
- Strategic Planning: Align your business strategies, goals, and resource allocation with the identified trends and forecasts.
- Product Development: Develop new products or adapt existing ones to cater to emerging market needs and trends.
- Marketing Strategies: Tailor marketing campaigns to address current trends and consumer preferences.
- Risk Management: Use forecasts to identify potential risks and create contingency plans.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor industry trends and update forecasts as market conditions change.
Understanding industry trends and accurately forecasting market developments is a proactive approach to business success. By staying informed and making data-driven decisions, businesses can adapt to evolving market dynamics and seize opportunities for growth.
Chapter 9: Turning Market Intelligence into Action
Market Intelligence (MI) is only as valuable as the actions it inspires. Gathering data and insights is just the beginning; the true power of MI lies in its ability to inform and drive strategic decisions. In this chapter, we will explore the essential steps for translating MI into actionable strategies and tactics that lead to business growth and success.
- Define Clear Objectives: Before you can turn MI into action, it's essential to define clear objectives. What specific goals do you want to achieve with the information gathered through MI? These objectives will guide your decision-making process.
- Prioritize Insights: Not all insights gathered through MI are equally important or urgent. Prioritize the insights that align with your defined objectives and have the potential to make the most significant impact on your business.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Effective MI implementation often requires collaboration across different departments within your organization. Bring together cross-functional teams, including marketing, sales, product development, and customer service, to ensure alignment and buy-in.
- Create an Action Plan: Develop a detailed action plan that outlines the specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities for implementing MI insights. A well-defined plan ensures that actions are executed systematically.
- Allocate Resources: Allocate the necessary resources, including budgets, personnel, and technology, to support the execution of your MI-driven strategies. Adequate resourcing is critical for successful implementation.
- Implement Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Leverage MI to create highly targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments. Use customer personas and preferences to tailor messages and offers.
- Product and Service Enhancements: Based on MI insights, make improvements to your products or services to address customer pain points and align with emerging trends. Ensure that your offerings remain competitive and relevant.
- Pricing Strategies: Use MI to optimize pricing strategies. This may involve adjusting prices to match market conditions or offering discounts to target specific customer segments.
- Customer Engagement and Retention: Implement strategies to enhance customer engagement and retention. Leverage MI to identify opportunities to improve customer support, loyalty programs, and personalized experiences.
- Competitive Strategies: Develop competitive strategies based on insights gathered through Competitive Intelligence. Identify weaknesses in competitors and areas where you can outperform them.
- Monitor and Measure: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track the impact of your MI-driven actions. Regularly monitor progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Market conditions change, and MI must evolve with them. Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation within your organization. Stay open to new insights and be willing to adjust strategies as needed.
- Feedback Loops: Create feedback loops that allow your teams to provide insights and observations based on their interactions with customers and market dynamics. This information can help refine strategies over time.
- Risk Mitigation: Use MI to identify potential risks and challenges. Develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate these risks.
- Review and Refine: Regularly review the effectiveness of your MI-driven actions. If certain strategies are not delivering the expected results, be willing to refine or pivot your approach.
- Executive Buy-In: Ensure that top leadership within your organization supports MI-driven initiatives. Their buy-in is essential for securing the necessary resources and commitment.
- Training and Development: Invest in training and development programs for your teams to ensure they have the skills and knowledge needed to execute MI-driven strategies effectively.
Turning MI into action is an ongoing process that requires commitment, agility, and a customer-centric mindset. By taking deliberate steps to implement MI insights and continuously adapt to changing market conditions, your organization can unlock the full potential of Market Intelligence to drive growth and success.
Chapter 10: Challenges and the Future of Market Intelligence
As Market Intelligence (MI) continues to evolve in response to advancements in technology, changes in consumer behavior, and shifts in global markets, it also faces various challenges and uncertainties. In this chapter, we'll explore some of the key challenges currently faced by MI practitioners and discuss the potential future trends and developments in this field.
Challenges in Market Intelligence:
- Data Overload: The exponential growth of data presents a challenge in terms of processing and making sense of vast volumes of information. MI practitioners must develop efficient data management and analysis strategies.
- Data Privacy and Ethics: The increasing focus on data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, complicates data collection and usage. Ensuring compliance while gathering customer-centric data is a significant challenge.
- Information Overload: Information is readily available from numerous sources, but distinguishing valuable insights from noise can be challenging. Curation and filtering of relevant data are critical.
- Real-Time Data: The demand for real-time data to make timely decisions is growing. Organizations must invest in technologies and processes that enable rapid data collection and analysis.
- Competitive Intelligence in the Digital Age: With the proliferation of digital channels and the ease of online information sharing, gathering competitive intelligence without crossing ethical boundaries is a challenge.
- AI and Automation: While AI and automation offer powerful tools for MI, they also raise concerns about job displacement and the need for human expertise in data interpretation and strategy formulation.
- Interpreting Unstructured Data: A significant portion of valuable MI comes from unstructured data sources like social media and online reviews. Developing effective methods to interpret and analyze unstructured data is a challenge.
The Future of Market Intelligence:
- Advanced Analytics: The future of MI will likely see an increased reliance on advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to process and analyze data efficiently and identify deeper insights.
- Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: MI will move beyond descriptive analysis to predictive and prescriptive analytics. Businesses will use data to anticipate future trends and make proactive recommendations.
- Personalization: MI will enable highly personalized marketing and customer experiences by leveraging AI-driven recommendations and tailored messaging.
- Data Privacy Solutions: As data privacy regulations continue to evolve, there will be an increased focus on technologies and tools that help businesses collect and use data while ensuring compliance.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical use of MI will become a central concern, with businesses focusing on transparency, accountability, and responsible data practices.
- Real-Time Insights: The demand for real-time insights will grow, driving the development of technologies and platforms that provide up-to-the-minute data and analysis.
- Integration of Multiple Data Sources: MI will increasingly rely on integrating data from diverse sources, including online and offline sources, to create a comprehensive view of the market.
- Global Market Expansion: As businesses seek growth opportunities beyond their borders, MI will play a critical role in understanding and entering new markets.
- Competitive Intelligence Evolution: Competitive intelligence will become more sophisticated, with a focus on monitoring online activities, social media sentiment, and digital footprints of competitors.
- Human-AI Collaboration: MI practitioners will collaborate with AI systems, with AI assisting in data processing and pattern recognition, while humans provide context, strategic thinking, and ethical oversight.
In summary, the future of Market Intelligence is both exciting and challenging. As technology continues to advance, MI practitioners will need to adapt and evolve their strategies and tools to stay competitive and make the most of the ever-expanding world of data and information. Ethical considerations and responsible data practices will also become increasingly important as MI becomes more integrated into business decision-making processes.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.