Market Research Reports
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Research Reports
Chapter 2: Types of Market Research Reports
Chapter 3: The Importance of Market Research
Chapter 4: Gathering Market Data
Chapter 5: Analyzing Market Data
Chapter 6: Constructing Effective Reports
Chapter 8: Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis and Reporting
Chapter 9: Presenting Findings: Communicating Data-Driven Insights
Chapter 10: The Future of Market Research Reports
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Research Reports
Market research reports are invaluable tools for businesses and organizations seeking to make informed decisions in a rapidly evolving marketplace. These reports are comprehensive documents that provide detailed insights into various aspects of a specific market, industry, or consumer behavior. They are the result of systematic data collection, analysis, and interpretation, all aimed at helping businesses understand market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes.
Market research reports serve as a roadmap for businesses, guiding them through the complexities of today's markets. Whether you are launching a new product, expanding into new territories, or looking to refine your marketing strategy, market research reports can provide the data and analysis needed to make well-informed choices.
Market research key characteristics
Here are some key characteristics and components of market research reports:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Market research reports are based on data collected from various sources, including surveys, interviews, observations, and secondary research. This data is systematically analyzed to draw meaningful conclusions and insights.
- Objective Presentation: Market research reports aim to present information objectively, without bias or subjective interpretation. They provide factual data and analysis that can be used by businesses to make informed decisions.
- Structure: These reports typically follow a structured format, including sections such as an executive summary, methodology, findings, recommendations, and appendices. This structure makes it easy for readers to navigate and find the information they need.
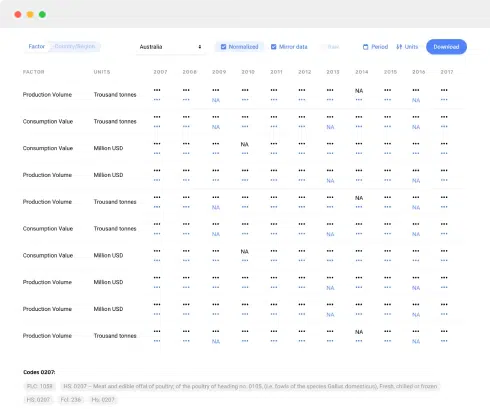
- Visual Aids: Visual elements like charts, graphs, and tables are often included to illustrate key findings and trends. Visual aids make complex data more accessible and understandable.
- Target Audience: Market research reports are created for specific target audiences, which may include business executives, investors, marketers, policymakers, or industry professionals. Reports are tailored to meet the needs and interests of these audiences.
- Market Segmentation: Reports often include market segmentation, which involves categorizing the market into distinct segments based on factors like demographics, geography, behavior, or product preferences. This segmentation helps businesses target specific customer groups effectively.
- Competitive Analysis: Many market research reports include a competitive analysis section, which examines the strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positions of key competitors in the industry.
- Recommendations: Reports often conclude with recommendations based on the research findings. These recommendations guide businesses on potential strategies, actions, or improvements that can be implemented.
- Customization: Some market research reports are customized to meet the specific needs of individual businesses or clients. Custom reports may focus on niche markets or address particular research questions.
- Timeliness: Market research reports are often updated regularly to reflect the latest market developments and trends. Businesses rely on up-to-date information to make timely decisions.
Market research reports are invaluable tools for businesses seeking to understand market dynamics, identify growth opportunities, assess risks, and develop effective strategies. They provide a data-driven foundation for decision-making, allowing organizations to stay competitive and responsive in ever-changing markets.
Why are they essential for businesses?
Market research plays a significant role in informed decision-making across various sectors and industries. It provides data and insights that guide businesses, organizations, and policymakers in making well-informed choices. Here are some key aspects of how market research contributes to informed decision-making:
Understanding the Market Environment: Market research helps businesses gain a deep understanding of the market in which they operate. This includes insights into market size, growth trends, customer demographics, and competitive landscapes. This knowledge is crucial for identifying opportunities and threats.
Identifying Customer Needs and Preferences: Research enables organizations to discern customer preferences, pain points, and expectations. By understanding what customers want and need, businesses can tailor their products, services, and marketing strategies to better meet these demands.
Assessing Market Viability: Before launching a new product or service, businesses use market research to assess its viability. Research helps determine if there is a demand for the offering and if it can be profitable in the current market conditions.
Risk Mitigation: Market research identifies potential risks and challenges that a business may encounter. By anticipating these issues, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate them or develop contingency plans.
Competitive Intelligence: Research allows businesses to analyze their competitors. By studying competitors' strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning, organizations can formulate strategies that give them a competitive advantage. Businesses use market intelligence platforms to conduct market research in a more accurate way.
Product Development and Innovation: Market research informs product development by uncovering insights about what customers want and need. It guides innovation efforts, helping businesses create products that resonate with their target audience.
Pricing and Positioning: Businesses use research to determine the optimal pricing strategy for their products or services. It helps establish the right balance between pricing and perceived value in the eyes of consumers.
Marketing Effectiveness: Research assesses the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and advertising efforts. It provides data on which marketing channels are most effective and which messages resonate with the target audience.
Expansion and Market Entry: When considering entering new markets or expanding operations, market research provides critical insights. It helps assess the feasibility of expansion and identifies entry barriers and potential challenges.
Policy and Strategy Development: Beyond business applications, market research informs government policymakers and nonprofit organizations in making decisions related to economic development, public policy, and social initiatives.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: In an era of big data, market research contributes to data-driven decision-making. It provides the evidence and analytics necessary to make informed choices rather than relying on intuition or guesswork.
Continuous Improvement: Market research is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regular research allows organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics and continuously improve their strategies and offerings.
In summary, market research is a fundamental tool for informed decision-making. It helps organizations gather and analyze data, understand their markets, customers, and competition, and make strategic choices that enhance their competitiveness, profitability, and overall success. By leveraging market research, businesses and decision-makers can reduce uncertainty, make evidence-based decisions, and navigate the complexities of today's rapidly changing business environments with greater confidence.
Chapter 2: Types of Market Research Reports
Market research reports come in various forms, each tailored to address specific business needs and objectives. Understanding the different types of reports is crucial as it helps businesses choose the most relevant and informative sources of information. In this chapter, we will explore the main types of market research reports:
- These reports provide a comprehensive overview of a particular industry.
- They include information on market size, growth trends, major players, and key challenges.
- Industry reports are invaluable for businesses looking to enter or invest in a specific sector.
2. Market Analysis Reports:
- Market analysis reports focus on a particular market or segment within an industry.
- They delve into consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns.
- These reports help businesses tailor their products and marketing strategies to target specific market segments effectively.
3. Competitive Analysis Reports:
- These reports examine the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in a given market.
- They provide insights into competitors' products, pricing, marketing strategies, and market share.
- Competitive analysis reports assist businesses in refining their competitive strategies.
4. Consumer Behavior Reports:
- Consumer behavior reports analyze how consumers make purchasing decisions.
- They explore factors such as demographics, psychographics, and buying motivations.
- These reports are essential for businesses aiming to understand and influence consumer choices.
5. Product Research Reports:
- Product research reports focus on a particular product or product category.
- They assess market demand, consumer preferences, and potential for innovation or improvement.
- These reports guide product development and enhancement efforts.
6. Market Entry and Expansion Reports:
- When considering entering new markets or expanding operations, these reports provide critical insights.
- They evaluate market potential, regulatory factors, and entry barriers.
- Market entry and expansion reports minimize risks associated with international or regional expansion.
7. Customer Satisfaction and Feedback Reports:
- These reports gauge customer satisfaction, loyalty, and feedback.
- They often include surveys and customer reviews.
- Customer satisfaction reports help businesses identify areas for improvement and maintain a loyal customer base.
8. Trend Analysis Reports:
- Trend analysis reports identify emerging trends and shifts in the market.
- They forecast changes in consumer behavior, technology, and industry dynamics.
- Businesses can adapt their strategies to capitalize on emerging trends.
Understanding these various types of market research reports allows businesses to choose the right ones to inform their strategic decisions. In the subsequent chapters, we will delve deeper into each report type, exploring their methodologies and applications in more detail.
Choosing the right market research report for your specific needs is essential for gaining valuable insights that drive informed decision-making. Market reports come in various formats, each tailored to different research objectives and industry sectors. To make the best choice, follow these steps:
- Define your research goals clearly.
- Identify your target audience.
- Understand your industry or market.
- Evaluate the scope of research.
- Examine report samples.
- Validate data sources.
- Confirm the report's currency.
- Assess the report's trustworthiness.
- Consider your budget constraints.
- Seek expert advice if needed.
- Read reviews and recommendations.
- Request a report preview or trial access.
Chapter 3: The Importance of Market Research
Market research is the foundation upon which successful business strategies are built. It plays a pivotal role in guiding organizations to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities. In this chapter, we will explore the significance and multifaceted importance of market research:
1. Informed Decision-Making:
Informed decision-making is the bedrock upon which successful organizations and individuals build their future. It involves the deliberate and systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and evaluating information to make choices that are grounded in facts, evidence, and a deep understanding of the situation.
2. Understanding Customer Needs:
Understanding customer needs is the cornerstone of building strong and enduring relationships with clients and consumers. It's a dynamic process that involves gaining deep insights into what customers desire, expect, and value.
3. Competitive Advantage:
Competitive advantage is the secret sauce that sets successful businesses apart from their rivals. It's the unique blend of strengths, strategies, and qualities that allow a company to outperform its competition.
4. Risk Mitigation:
Risk mitigation is a proactive strategy employed by organizations to identify, assess, and reduce potential risks that could impact their operations, goals, or projects. It's a critical component of effective risk management.
5. Identifying Market Opportunities:
Identifying market opportunities is a strategic process that allows businesses to uncover unmet needs, emerging trends, or gaps in the market that can be leveraged for growth.
6. Efficient Resource Allocation:
Efficient resource allocation is the art of deploying available resources—such as finances, manpower, and time—in a way that optimizes their impact and aligns with strategic objectives.
7. Product Development and Innovation:
Product development and innovation are twin engines that drive a company's growth, competitiveness, and ability to meet evolving customer demands.
8. Marketing Effectiveness:
Marketing effectiveness is the measure of how well a company's marketing strategies and campaigns achieve their intended goals.
9. Adaptation to Market Changes:
The ability to adapt to market changes is a fundamental survival skill for businesses in today's rapidly evolving environment.
10. Long-Term Sustainability:
Long-term sustainability is the compass that guides businesses toward a future marked by resilience, responsible growth, and lasting success.
In essence, market research is a cornerstone of successful business operations. It empowers organizations to make decisions based on evidence rather than assumptions, resulting in more effective strategies, improved competitiveness, and sustained growth. As we delve further into this book, you will gain a deeper appreciation for how market research reports are essential tools for achieving these objectives.
Chapter 4: Gathering Market Data
Market research reports are only as good as the data upon which they are built. In this chapter, we will explore the crucial process of gathering market data, which forms the foundation of insightful reports. Effective data collection ensures the accuracy and reliability of the information presented in these reports.
1. Primary Data Sources:
- Primary data is data collected firsthand by the researcher.
- Methods include surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments.
- Primary data sources provide fresh and specific insights directly from the target audience.
2. Secondary Data Sources:
- Secondary data is pre-existing data collected by others, such as government agencies, industry associations, or previous research studies.
- It can include market reports, academic papers, and publicly available data.
- Secondary data sources are cost-effective and offer historical context.
3. Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Surveys involve the systematic collection of responses to structured questions.
- They can be administered through online surveys, phone interviews, or in-person questionnaires.
- Surveys are highly customizable and are used to gather opinions, preferences, and demographic data.
4. Interviews:
- Interviews involve direct conversations with individuals or groups.
- They can be structured (using predetermined questions) or unstructured (allowing for open-ended discussions).
- Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics and gaining in-depth insights.
5. Observations:
- Observational research involves systematically watching and recording behaviors or events.
- It is often used in retail settings or ethnographic studies.
- Observations provide objective data on actual behavior.
6. Experiments:
- Experiments involve manipulating variables to test hypotheses.
- They are common in product testing and marketing studies.
- Experiments allow for causal relationships to be established.
7. Online Data Collection:
- The internet offers numerous opportunities for data collection.
- Social media, website analytics, and online surveys are examples.
- Online data collection is efficient for reaching large and geographically dispersed audiences.
8. Focus Groups:
- Focus groups are small, structured discussions with a select group of participants.
- They facilitate qualitative data collection and are often used for product testing and concept evaluation.
9. Data Validation and Quality Control:
- Ensuring data accuracy and reliability is essential.
- Validation methods include cross-referencing data with multiple sources and using statistical techniques to identify outliers.
10. Ethical Considerations:
- When gathering data, ethical guidelines must be followed.
- These include obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant anonymity, and handling sensitive information responsibly.
Effective data gathering is the first step in producing reliable and insightful market research reports. Whether you choose primary or secondary sources, or a combination of both, the quality of your data directly impacts the quality of your report's findings and recommendations. In subsequent chapters, we will delve into data analysis and how to transform raw data into meaningful insights.
Chapter 5: Analyzing Market Data
Basic Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover meaningful information, draw conclusions, and support decision-making. Here are some fundamental data analysis techniques that form the cornerstone of effective data-driven decision-making:
1. Descriptive Statistics:
- Descriptive statistics provide a snapshot of data's main characteristics. They include measures like mean (average), median (middle value), mode (most frequent value), and standard deviation (spread of data). These statistics help summarize and understand data distributions.
2. Data Visualization:
- Data visualization uses charts, graphs, and plots to represent data visually. It aids in identifying patterns, trends, and outliers that may not be apparent in raw data. Common visualizations include bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and heatmaps.
3. Histograms and Frequency Distributions:
- Histograms display the distribution of data by dividing it into bins or intervals and counting the frequency of values within each bin. They are especially useful for understanding the shape and spread of data.
4. Crosstabulation and Pivot Tables:
- These techniques are used for exploring relationships between categorical variables. Crosstabulation creates contingency tables that show the frequency of data points within different categories, while pivot tables summarize data in a tabular format.
5. Correlation Analysis:
- Correlation analysis measures the strength and direction of relationships between two continuous variables. The correlation coefficient (e.g., Pearson's correlation coefficient) quantifies the degree of association between variables, helping identify potential connections.
6. Regression Analysis:
- Regression analysis assesses the relationship between one or more independent variables and a dependent variable. It helps predict outcomes and understand the impact of different factors on a specific outcome.
7. Hypothesis Testing:
- Hypothesis testing involves making statistical inferences about a population based on sample data. It allows researchers to determine whether observed differences or relationships are statistically significant or due to chance.
8. Time Series Analysis:
- Time series analysis focuses on data collected over time, such as stock prices, sales figures, or weather data. Techniques like moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models help identify trends and patterns.
9. Clustering and Segmentation:
- Clustering techniques group similar data points together based on predefined criteria, while segmentation divides a dataset into subsets with shared characteristics. These methods are commonly used in marketing and customer segmentation.
10. Text Mining and Sentiment Analysis:
- Text mining extracts valuable insights from unstructured text data, such as social media comments or customer reviews. Sentiment analysis assesses sentiment or emotion expressed in text, providing insights into public opinion.
11. Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
- Before analysis, data often needs cleaning to handle missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. Data preprocessing involves transforming and normalizing data for better analysis outcomes.
12. Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
- GIS techniques analyze spatial data, such as maps and geographical information. They are used in fields like urban planning, environmental science, and logistics to make location-based decisions.
These basic data analysis techniques form the foundation for more advanced analytics and data science methods. They empower organizations and individuals to extract valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and gain a competitive edge in a data-rich world.
Tools and software for analysis
There is a wide range of tools and software available for data analysis, catering to various needs and skill levels. Here are some popular options across different categories:
1. Spreadsheet Software:
- Microsoft Excel: A versatile spreadsheet tool widely used for data analysis, visualization, and basic statistical functions.
- Google Sheets: Google's cloud-based spreadsheet tool, similar to Excel, with collaborative features.
2. Statistical Analysis Software:
- R: An open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics, favored by statisticians and data scientists.
- Python with Libraries (e.g., NumPy, Pandas, SciPy): Python is a versatile programming language often used for data analysis, and these libraries provide powerful data manipulation and analysis capabilities.
- SPSS: Statistical software used for advanced statistical analysis, particularly in social sciences and research.
- SAS: Software suite for advanced analytics, business intelligence, and data management.
3. Business Intelligence (BI) Tools:
- Tableau: A leading BI and data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards.
- Power BI: Microsoft's business analytics service for creating interactive reports and visualizations.
- QlikView/Qlik Sense: BI tools for data discovery, interactive dashboards, and self-service analytics.
4. Data Visualization Tools:
- Tableau: Known for its powerful data visualization capabilities.
- D3.js: A JavaScript library for creating interactive data visualizations on the web.
- Plotly: A Python and JavaScript graphing library for creating interactive plots and dashboards.
5. Data Mining and Machine Learning Tools:
- Weka: An open-source data mining tool with a graphical user interface.
- RapidMiner: An open-source data science platform offering a wide range of data analysis and machine learning capabilities.
6. Data Cleaning and Preparation Tools:
- OpenRefine: An open-source tool for cleaning and transforming messy data.
- Trifacta: A data wrangling platform that simplifies data cleaning and preparation tasks.
7. Geographic Information System (GIS) Software:
- ArcGIS: A popular GIS software suite for mapping, spatial analysis, and geospatial data management.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS software that offers a wide range of mapping and spatial analysis capabilities.
8. Text Analytics and Natural Language Processing (NLP) Tools:
- NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit): A Python library for working with human language data, including text analysis and NLP.
- Stanford NLP: A suite of NLP tools and libraries developed by Stanford University.
9. Big Data and Cloud-Based Tools:
- Hadoop: An open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of big data.
- Apache Spark: A fast and general-purpose cluster computing system that works seamlessly with big data.
- Google Cloud BigQuery: A fully managed, serverless data warehouse for big data analytics.
- Amazon Redshift: A cloud-based data warehousing solution for data analysis.
10. Data Science Platforms: - IBM Watson Studio: An integrated environment for data science, machine learning, and AI. - DataRobot: An automated machine learning platform that streamlines the modeling process.
The choice of tool or software depends on factors such as the specific data analysis tasks, your proficiency in using them, and budget constraints. Many tools offer free trials or open-source options, allowing you to explore and determine the best fit for your needs.
Chapter 6: Constructing Effective Reports
Constructing effective reports is essential for conveying data-driven insights, recommendations, and findings to various stakeholders. Whether you're preparing a business report, research paper, or project update, here are key principles to ensure your reports are clear, informative, and impactful:
1. Define Your Purpose:
Clarify the report's purpose and objectives. What do you aim to achieve with this report, and who is your target audience? Understanding these aspects is the first step in effective reporting.
2. Organize Content Logically:
Structure your report with a logical flow. Typically, reports include sections like an executive summary, introduction, methodology, findings, analysis, recommendations, and conclusion. This structure guides readers through the information smoothly.
3. Craft a Compelling Executive Summary:
Start with a concise executive summary that encapsulates the main points and key findings. This section should provide a snapshot of the entire report, allowing busy stakeholders to grasp the essence quickly.
4. Use Clear and Concise Language:
Write in clear, plain language. Avoid jargon, technical terms, or excessive complexity unless your audience is familiar with the terminology. Aim for clarity and brevity.
5. Visualize Data Effectively:
Incorporate visuals such as charts, graphs, tables, and infographics to illustrate key points. Ensure that these visuals are well-labeled and easy to interpret. Choose the right type of visualization for your data.
6. Provide Context and Background:
Offer context and background information to help readers understand the significance of the report. Explain the problem or situation, the research methodology, and any relevant historical or industry context.
7. Present Findings Objectively:
Present findings objectively, supported by data and evidence. Be transparent about the limitations of the data or research methods used.
8. Interpret Data and Analysis:
Interpret data and analysis by explaining the implications of your findings. What do the numbers or trends mean for the organization or project? Provide insights and actionable takeaways.
9. Offer Clear Recommendations:
If applicable, provide clear and actionable recommendations based on your analysis. These recommendations should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the report's objectives.
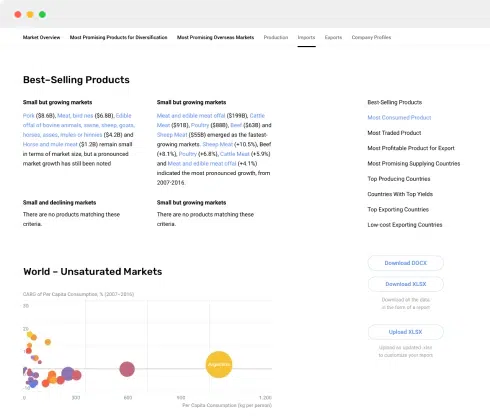
Include Supporting Appendices: - Complex data, additional details, or supplementary materials can be placed in appendices. Reference these appendices in the main report as needed.
Review and Edit Carefully: - Proofread and edit your report thoroughly to eliminate errors in grammar, punctuation, and formatting. A well-polished report enhances professionalism.
Consider Visual Design: - Pay attention to the visual design of your report. Use consistent fonts, headings, and formatting. Ensure that the report is visually appealing and easy to navigate.
Tailor for the Audience: - Customize the report's tone, depth, and technicality to match the audience's level of expertise and interests. Tailoring ensures that the report resonates with its intended readers.
Seek Feedback: - Before finalizing the report, seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or subject matter experts. Fresh perspectives can help improve the report's quality.
Test for Readability: - Assess the report's readability by considering factors like sentence length, paragraph structure, and overall readability scores. Tools like the Flesch-Kincaid Readability Test can assist in this regard.
Constructing effective reports is an art that combines data analysis, communication skills, and a clear understanding of your audience. A well-constructed report not only conveys information but also empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the insights you provide.
Chapter 7: Visualizing Data
In the world of data analysis and reporting, visualizing data is an indispensable tool for effectively conveying complex information, trends, and patterns. Visualizing data goes beyond mere aesthetics; it's about transforming numbers and statistics into visual narratives that can be easily understood and remembered.
Visualizations aid in data analysis by revealing patterns, trends, outliers, and correlations that may not be immediately apparent in raw data. They help analysts explore and interpret data more efficiently. Well-designed visualizations provide decision-makers with a clear and concise overview of key insights. This aids in making informed decisions and taking timely action.
Visualizations enable data storytellers to convey narratives that engage and resonate with the audience. They turn data into compelling stories that leave a lasting impression. Additionally, visuals are language-agnostic and can transcend language barriers, making them suitable for diverse global audiences.
Creating effective data visualizations requires a thoughtful approach and adherence to best practices. Here are some key principles to keep in mind:
Choose the appropriate chart or graph type that best suits the data and the message you want to convey. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and heatmaps.
Keep visualizations simple and avoid clutter. Focus on the most critical data points and eliminate unnecessary elements that can distract from the message.
Ensure that labels, titles, legends, and axes are clear and concise. Proper labeling is essential for understanding the context of the visualization.
Choose color palettes that enhance readability and convey meaning. Avoid overly bright or contrasting colors that can be distracting.
Always include context, such as captions or annotations, to explain the significance of the visualization and guide the reader's interpretation.
Maintain a consistent style and format across visualizations within the same report. This helps readers navigate and compare different charts and graphs more easily.
Ensure that your visualizations are accessible to all readers, including those with visual impairments. Use alt text for images, provide textual summaries, and consider color-blind-friendly designs.
Don't be afraid to iterate and refine your visualizations based on feedback and changing requirements. Continuous improvement leads to more effective communication.
In conclusion, visualizing data is an art and a science that plays a pivotal role in modern reporting. When done well, data visualization transforms data into insights, enabling more informed decisions and engaging storytelling. In the next chapter, we'll explore ethical considerations in data analysis and reporting, emphasizing the importance of responsible data handling.
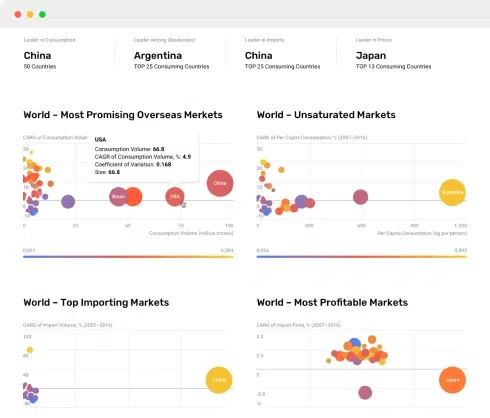
Charts, Graphs, and Infographics: Visualizing Information with Impact
In the realm of data communication and storytelling, charts, graphs, and infographics serve as dynamic tools to convey complex information effectively. These visual representations bring data to life, making it accessible, memorable, and actionable. Here's a closer look at the significance of these visual aids:
The Power of Charts and Graphs:
Charts and graphs are fundamental to data visualization, offering numerous benefits for presenting information:
- Clarity and Simplicity: Charts and graphs distill complex data into clear, easily digestible visuals. They simplify information, enabling readers to grasp key points at a glance.
- Comparison and Trends: Line graphs, bar charts, and scatter plots facilitate the comparison of data points and the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies.
- Data Relationships: Visuals like scatter plots reveal relationships between variables, helping analysts explore correlations and causation.
- Time Series Analysis: Line graphs are particularly useful for representing data over time, making them valuable for tracking trends, seasonal variations, and forecasting.
- Distribution and Frequency: Histograms and box plots illustrate data distribution and frequency, providing insights into data spread and central tendencies.
- Geospatial Insights: Maps and geographic charts visualize data by location, enabling the understanding of regional variations and trends.
Infographics:
Infographics take data visualization to another level by combining text, visuals, and design elements to convey complex information in a concise and engaging format:
- Storytelling: Infographics tell a visual story, guiding the audience through a narrative that simplifies and clarifies intricate data and concepts.
- Engagement: The combination of text and visuals in infographics captures readers' attention and encourages them to explore and understand the information presented.
- Memorability: Infographics are memorable because they leverage visual memory cues. Readers are more likely to recall key points presented in this format.
- Versatility: Infographics can cover a wide range of topics, from data-driven insights and statistics to explanatory diagrams and step-by-step guides.
- Shareability: Infographics are highly shareable on social media and other online platforms, making them an effective tool for disseminating information to a broader audience.
Best Practices:
To harness the full potential of charts, graphs, and infographics, consider the following best practices:
- Choose the Right Visual: Select the appropriate chart or graphic type that aligns with your data and message.
- Simplify and Focus: Keep visuals clean and uncluttered, emphasizing the most critical information.
- Label Clearly: Ensure all elements, including axes, data points, and legends, are well-labeled for easy comprehension.
- Color with Purpose: Use colors strategically to convey meaning, but avoid overwhelming or confusing color schemes.
- Provide Context: Include titles, captions, and explanatory notes to offer context and guide interpretation.
- Accessibility: Design visuals with accessibility in mind, making them inclusive for all audiences.
- Test and Iterate: Seek feedback and be willing to iterate and refine your visuals to enhance their effectiveness.
In summary, charts, graphs, and infographics are indispensable tools for conveying information, engaging audiences, and fostering understanding. When applied thoughtfully and strategically, these visual aids empower effective communication and storytelling in a data-driven world.
Chapter 8: Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis and Reporting
In the realm of data analysis and reporting, ethical considerations are of paramount importance. This chapter underscores the ethical principles that should guide data professionals, researchers, and organizations in their data-related endeavors. Upholding ethical standards in data analysis and reporting is not just a matter of compliance with laws and regulations; it's a fundamental commitment to fairness, transparency, privacy protection, and responsible data use.
The Significance of Ethical Data Handling:
Ethical conduct in data analysis and reporting is significant for several compelling reasons:
Ethical data practices build trust and credibility with stakeholders, including customers, clients, and the public. When individuals and organizations know that their data is handled with integrity, they are more likely to have confidence in data-driven insights.
Ethical behavior ensures legal compliance with data protection and privacy laws. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) require organizations to adhere to ethical data practices.
Respecting individual privacy is a cornerstone of ethical data handling. It involves safeguarding sensitive and personally identifiable information from unauthorized access, sharing, or misuse.
Ethical data practices aim to minimize biases that can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This is particularly crucial in fields such as hiring, lending, and criminal justice, where data-driven decisions impact individuals' lives.
Informed consent is central to ethical data collection. Individuals whose data is being gathered should be fully informed about the purpose of data collection and any potential implications.
Data security is an integral part of ethical conduct. Robust data security measures protect data from breaches, unauthorized access, or cyberattacks. Encrypting sensitive data and restricting access to authorized personnel are key components.
Ethical reporting involves accurately representing data, avoiding selective reporting, and refraining from misrepresenting findings to advance specific agendas. It upholds the principles of honesty and transparency in reporting.
Best Practices for Ethical Data Handling:
To ensure ethical data analysis and reporting, consider the following best practices:
Transparency is essential. Be open about data sources, collection methods, and any potential biases in the data. Provide clear explanations of how data was obtained and processed.
When collecting data from individuals, obtain informed consent. Explain the purpose of data collection and any potential implications.
Protect individual privacy by anonymizing or de-identifying data when necessary. Remove or encrypt personally identifiable information (PII) to prevent privacy breaches.
Scrutinize data and algorithms for biases that could lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Implement measures to mitigate bias in data analysis and reporting.
Implement robust data security measures to safeguard data from breaches or unauthorized access. Encryption and access restrictions are critical components of data security.
Maintain integrity in reporting. Ensure that data is accurately represented, avoid cherry-picking results, and disclose potential conflicts of interest.
Comply with data protection and privacy laws relevant to your jurisdiction and industry. Stay informed about regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, and ensure your practices align with these laws.
Promote continuous education on ethical considerations in data analysis and reporting. Foster a culture of ethical data use within your organization.
In conclusion, ethical considerations are the foundation of responsible data analysis and reporting. Upholding ethical standards is not only a legal requirement but also a moral imperative that ensures the respectful and responsible treatment of individuals' data. By integrating ethical practices into data handling, organizations can build trust, enhance credibility, and contribute to a more ethical and equitable data-driven world.
Chapter 9: Presenting Findings: Communicating Data-Driven Insights
In the data-centric landscape of today's business and research environments, the art of presenting findings holds a crucial role in ensuring that data-driven insights are not just understood but also acted upon effectively. This chapter underscores the significance of presenting findings in a manner that fosters clarity, engagement, and actionable decision-making.
The Significance of Presenting Findings:
Presenting findings is not a mere formality in the data analysis process; it is a pivotal step with profound implications:
1. Clarity and Understanding:
- Effective presentations distill complex data and analysis into a comprehensible narrative. They bridge the gap between raw data and meaningful insights.
2. Engagement and Attention:
- Well-structured and engaging presentations capture the audience's attention, sustaining their interest and facilitating better understanding and retention of key takeaways.
3. Informed Decision-Making:
- Presentations serve as a conduit for informed decision-making. They empower stakeholders to make choices rooted in data-driven insights rather than intuition or conjecture.
4. Actionability:
- The ultimate goal of presenting findings is to inspire action. A compelling presentation motivates the audience to act on the insights presented, driving positive outcomes.
Best Practices for Presenting Findings:
To ensure that your findings are effectively communicated and have the desired impact, consider the following best practices:
1. Know Your Audience:
Tailor your presentation to the specific needs, interests, and knowledge level of your audience. Understanding their priorities and perspectives is crucial in shaping your message.
2. Structure and Flow:
Organize your presentation logically, creating a coherent narrative with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Use storytelling techniques to guide the audience through the data and insights.
3. Visual Aids:
Enhance comprehension and engagement by incorporating visuals such as charts, graphs, and infographics. Visual aids provide a visual context that complements the spoken narrative.
4. Storytelling:
Frame your presentation as a story. Utilize anecdotes, examples, and relatable scenarios to create a connection with your audience and make the data more relatable and memorable.
5. Clarity and Simplicity:
Prioritize clear and concise communication. Avoid industry jargon or technical language that may alienate your audience. Keep slides uncluttered and focused on key points.
6. Engage the Audience:
Foster interaction and engagement throughout the presentation. Encourage questions, seek feedback, and facilitate discussions to maintain the audience's involvement.
7. Highlight Key Insights:
Focus on the most pivotal findings and insights. Avoid overwhelming the audience with an excess of data points, instead emphasizing those that are most relevant to your message.
8. Data Interpretation:
Go beyond data presentation; interpret the data and articulate its significance. Help the audience not only understand what the data shows but also grasp its implications for the organization or project.
9. Address Questions and Concerns:
Be prepared to respond to questions and address concerns. Anticipate potential queries and have supporting evidence and explanations ready to provide clarity.
10. Actionable Recommendations:
If relevant, provide clear and actionable recommendations based on the findings. Ensure that these recommendations align with the objectives of your presentation.
11. Practice and Rehearse:
Ensure a polished delivery by rehearsing your presentation multiple times. Consider seeking feedback from colleagues or mentors to refine your delivery further.
12. Visual Design:
Attend to the visual design of your presentation slides. Maintain consistency in fonts, color schemes, and formatting for a professional and cohesive look.
13. Time Management:
Respect the allocated time for your presentation. Be concise and adhere to the schedule to avoid losing the audience's interest.
14. Follow-Up:
After the presentation, continue engagement with the audience. Address any additional questions or provide supplementary information as needed to support their understanding and decision-making process.
In conclusion, presenting findings is not a mere formality but a vital step in ensuring that data-driven insights are not just heard but acted upon. By adhering to best practices that prioritize clear communication, engagement, and actionability, you can maximize the impact of your presentations and drive positive change based on data-driven insights.
Chapter 10: The Future of Market Research Reports
In the rapidly evolving realm of market research, the future of market research reports holds both exciting opportunities and unique challenges. This chapter explores the evolving landscape of market research reports, highlighting emerging trends, technologies, and strategies that will shape the future of this essential business intelligence tool.
The Evolving Landscape of Market Research Reports:
Market research reports have undergone significant transformations, reflecting changes in technology, consumer behavior, and business dynamics. Here's a glimpse into the evolving landscape:
1. Real-Time Insights:
The future of market research reports is marked by the transition from static snapshots to real-time insights. Advanced analytics and data streaming technologies enable businesses to access up-to-the-minute data for agile decision-making.
2. AI-Powered Analytics:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing market research. AI-driven algorithms can process vast datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and provide predictive analytics, enhancing the depth and accuracy of reports.
3. Personalization:
Market research reports are becoming more tailored to individual client needs. Advanced algorithms can customize reports to deliver insights relevant to specific industries, regions, or market segments.
4. Interactive Reports:
The future of market research reports may see the widespread adoption of interactive formats. These reports allow users to explore data dynamically, drill down into specific insights, and customize visualizations to suit their preferences.
5. Integration of Multiple Data Sources:
Modern market research reports combine data from various sources, such as social media, IoT devices, and traditional surveys, to provide a comprehensive view of market trends and consumer sentiment.
6. Sustainability and ESG Metrics:
Ethical and sustainable practices are increasingly vital considerations for businesses. Market research reports of the future may incorporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics to assess an organization's impact and reputation.
7. Enhanced Data Privacy:
As data privacy concerns continue to grow, the future of market research reports will prioritize robust data protection measures and transparent data collection practices to ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
8. Augmented and Virtual Reality:
Emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are opening new avenues for immersive data visualization, allowing users to explore market data in three-dimensional virtual environments.
9. Blockchain for Data Security:
Blockchain technology is being explored for enhancing the security and integrity of market research data. It can provide an immutable ledger for tracking data sources and ensuring data authenticity.
10. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: - Market research reports of the future will not only describe historical trends but also offer predictive and prescriptive insights, helping businesses anticipate market shifts and make informed decisions.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the future of market research reports promises innovation and value, there are challenges to navigate:
Data Privacy and Ethics: Striking a balance between data access and privacy will be crucial, as ethical concerns continue to shape data collection and usage practices.
Technological Adaptation: Keeping pace with evolving technologies and integrating them effectively into market research processes will be a challenge for many organizations.
Data Integration: Managing and integrating diverse data sources, from structured to unstructured, will require advanced data management and analytics capabilities.
Skills and Training: The workforce will need to acquire new skills to harness the potential of AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics in market research.
Conclusion:
The future of market research reports is dynamic and promising. As businesses seek deeper insights, greater personalization, and real-time information, market research professionals must adapt to new technologies and ethical considerations. By embracing these changes, market research reports will continue to be indispensable tools for informed decision-making in a rapidly changing business landscape
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.