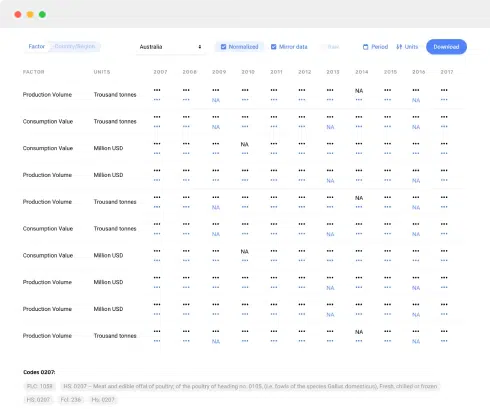
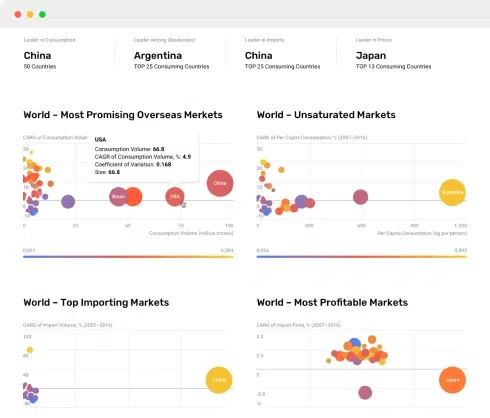
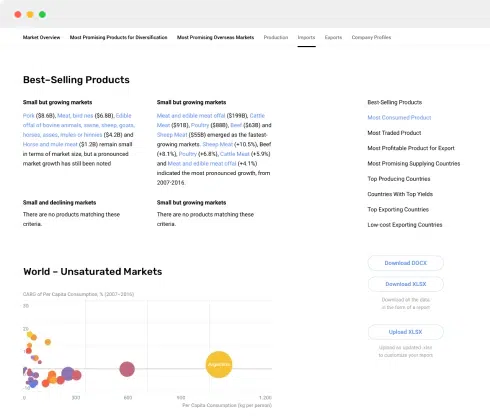
Industry Research
Industry research is a systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information and data related to a specific industry or market. It plays a vital role in helping businesses, organizations, investors, and policymakers make informed decisions. Industry research provides insights into market dynamics, trends, competition, consumer behavior, and other factors that influence business operations and strategies.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Industry Research
Chapter 2: Understanding the Basics of Industry Analysis
Chapter 3: The Role of Industry Research in Strategic Planning
Chapter 4: Gathering Primary Data for Industry Research
Chapter 5: Analyzing Secondary Data in Industry Research
Chapter 6: Competitive Analysis in Industry Research
Chapter 7: Industry Trends and Forecasting
Chapter 8: Ethical Considerations in Industry Research
Chapter 9: Emerging Technologies in Industry Research
Chapter 10: The Future of Industry Research: Trends and Challenges
Chapter 1: Introduction to Industry Research
In a rapidly changing global business landscape, the importance of industry research cannot be overstated. Industry research serves as the foundation upon which informed business decisions are built. It is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data and information related to a specific industry or market sector. In this introductory chapter, we will explore the fundamental concepts, significance, and objectives of industry research.
The Significance of Industry Research:
Free industry research reports play a pivotal role in the success of businesses, organizations, and investors. Its significance can be summarized in several key points:
- Informed Decision-Making: Industry research provides decision-makers with the knowledge and insights needed to make informed and strategic choices. Whether it's entering a new market, launching a product, or allocating resources, research serves as the compass guiding decisions.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential risks, challenges, and market dynamics, industry research allows businesses to proactively develop strategies to mitigate these risks. It minimizes the element of surprise.
- Competitive Advantage: Understanding industry trends, competitor strategies, and customer behaviors enables organizations to gain a competitive edge. It helps in positioning products or services effectively.
- Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses seeking to expand into new markets or sectors, industry research is essential. It provides the necessary groundwork to navigate unfamiliar terrain.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient allocation of resources, whether financial, human, or technological, depends on accurate market information. Industry research ensures that resources are deployed optimally.
Objectives of Industry Research:
The primary objectives of industry research encompass a range of goals aimed at gaining comprehensive insights into the market and its dynamics:
- Understanding Market Size and Growth Potential: Industry research aims to determine the current market size, as well as its growth prospects. This information helps businesses identify opportunities for expansion.
- Market Segmentation: By segmenting the market based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences, industry research enables businesses to target specific customer groups effectively.
- Competitor Analysis: Understanding competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning is a key objective. This analysis informs businesses on how to outmaneuver rivals.
- Consumer Behavior and Preferences: Industry research delves into customer behaviors, buying patterns, and preferences. This insight is invaluable for product development and marketing strategies.
- Regulatory and Environmental Factors: Businesses must be aware of regulatory changes and environmental factors that may impact their operations. Industry research helps in assessing compliance and sustainability.
- Identifying Trends and Opportunities: Recognizing emerging trends and market opportunities allows organizations to adapt and innovate proactively.
- Risk Assessment: Industry research involves evaluating potential risks, such as economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or technological changes, and developing strategies to mitigate them.
The Research Process:
Industry research is a structured process that typically involves data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It relies on various data sources, including primary research (surveys, interviews, observations) and secondary research (existing reports, publications, databases).
Throughout this book, we will delve into the methodologies, tools, and best practices for conducting industry research effectively. From data gathering to competitive analysis and market forecasting, each chapter will provide valuable insights and practical guidance to help you navigate the world of industry research.
In the following chapters, we will explore the different facets of industry research, from data collection and analysis to the utilization of research findings in strategic decision-making. The knowledge and skills you gain will empower you to navigate the complexities of today's dynamic business environments.
Chapter 2: Understanding the Basics of Industry Analysis
Industry analysis is a foundational step in the process of gaining insights into a specific sector or market. It involves a systematic examination of the factors, trends, and dynamics that shape an industry. In this chapter, we will delve into the basics of industry analysis, exploring its purpose, key components, and methodologies.
The Purpose of Industry Analysis:
The primary purpose of industry analysis is to gain a comprehensive understanding of an industry's structure, trends, and competitive landscape. This understanding serves several crucial purposes:
- Strategic Decision-Making: Industry analysis provides the information necessary for informed and strategic decision-making. It guides organizations in setting goals, allocating resources, and planning for the future.
- Risk Assessment: By identifying potential risks and challenges within an industry, businesses can develop strategies to mitigate these risks effectively. This proactive approach helps in minimizing uncertainties.
- Competitive Advantage: Industry analysis allows organizations to identify opportunities for differentiation and competitive advantage. It helps in positioning products, services, and marketing efforts effectively.
- Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses considering entering a new market or expanding their operations, industry analysis is essential. It provides insights into market conditions and potential barriers.
Key Components of Industry Analysis:
Industry analysis comprises several key components, each offering valuable insights into the industry's dynamics:
- Industry Definition and Scope: Begin by defining the industry you are analyzing. Determine the scope of the analysis, including whether it covers a specific sector, region, or market niche.
- Market Size and Growth: Assess the current market size and growth rate. This information helps in gauging the industry's overall potential.
- Market Segmentation: Divide the market into segments based on criteria like demographics, geography, or product types. This segmentation enables businesses to target specific customer groups effectively.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze competitors within the industry. Identify key players, their market share, strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Customer Analysis: Understand customer behaviors, preferences, and buying patterns. This analysis guides product development and marketing strategies.
- Regulatory and Environmental Factors: Assess the regulatory landscape and environmental factors that impact the industry. This includes compliance requirements, sustainability concerns, and potential legal hurdles.
- Technological Trends: Investigate technological advancements and trends that are shaping the industry. This information is crucial for staying competitive and innovative.
- Economic Factors: Evaluate economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and consumer spending patterns, that affect the industry's performance.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Examine the supply chain, including suppliers, distributors, and logistics. Supply chain disruptions can impact industry stability.
Methodologies for Industry Analysis:
Industry analysis can be conducted using various methodologies, including:
- Desk Research: Desk research involves gathering information from existing sources, such as industry reports, publications, and databases. It provides a foundational understanding of the industry.
- Primary Research: Primary research involves collecting original data through methods like surveys, interviews, and observations. It allows for a more customized and in-depth analysis.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a structured framework for assessing an industry's internal and external factors. It helps in identifying strategic insights.
- Porter's Five Forces: Porter's Five Forces is a framework that assesses the competitive forces within an industry, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry.
- PESTEL Analysis: PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) analysis examines the macro-environmental factors affecting an industry. It provides a broad context for analysis.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing your organization's performance and metrics to those of competitors or industry leaders. It helps identify areas for improvement.
Understanding the basics of industry analysis is the foundation upon which more advanced research and strategic decision-making are built. In the subsequent chapters, we will explore these methodologies and components in greater detail, providing practical guidance for conducting effective industry analysis.
Chapter 3: The Role of Industry Research in Strategic Planning
Industry research plays a pivotal role in the strategic planning process of businesses and organizations. It provides the essential insights and data needed to formulate informed and effective strategies that can drive success and growth. In this chapter, we will explore in depth the critical role that industry research plays in shaping strategic planning.
Strategic Planning: A Holistic Approach
Strategic planning is the process by which organizations define their goals, allocate resources, and outline a roadmap to achieve their objectives. Effective strategic planning is a multidimensional approach that takes into consideration both internal and external factors. Industry research is a crucial element of this process as it provides valuable external insights.
Key Roles of Industry Research in Strategic Planning:
- Market Assessment: Industry research helps organizations assess the current market conditions, including its size, growth rate, and segmentation. This information serves as a foundation for setting realistic market penetration goals.
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding the competitive landscape through industry research enables organizations to identify key competitors, their strategies, and their strengths and weaknesses. This knowledge informs competitive positioning and differentiation strategies.
- Risk Mitigation: Industry research identifies potential risks and challenges within the market or industry, allowing organizations to develop contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
- Opportunity Identification: Industry research reveals emerging trends, market gaps, and customer needs that present opportunities for growth and innovation. It helps organizations capitalize on these opportunities.
- Resource Allocation: Strategic planning involves allocating resources, such as budgets, personnel, and technology, to various initiatives. Industry research ensures that resources are directed towards initiatives that align with market dynamics and opportunities.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Based on industry research, organizations can set clear and measurable objectives for their strategic initiatives. These objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
The Strategic Planning Process:
- Data Gathering: Industry research is the first step in the strategic planning process. It involves collecting relevant data and information about the industry, market, competitors, customers, and external factors.
- Analysis: The gathered data is then analyzed to identify trends, opportunities, threats, and areas for strategic focus. This analysis informs the development of strategic goals and objectives.
- Goal Setting: Based on the insights gained from industry research and analysis, organizations set clear and achievable strategic goals. These goals are aligned with the organization's mission and vision.
- Strategy Formulation: Industry research helps in formulating strategies that address market dynamics and leverage opportunities. These strategies outline the actions and initiatives required to achieve the set goals.
- Implementation: Once strategies are formulated, they are put into action. This stage involves the allocation of resources, project management, and execution of initiatives.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Ongoing monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) and progress toward strategic goals is essential. Industry research continues to play a role in evaluating whether strategies are effective or require adjustment.
- Adaptation: As market conditions and industry dynamics change, organizations must adapt their strategies accordingly. Industry research remains an integral part of this adaptive process.
Ethical Considerations:
Incorporating ethical considerations into industry research and strategic planning is paramount. Organizations must ensure that their strategies and actions align with ethical standards and responsible business practices. This includes ethical data collection, privacy considerations, and transparency in decision-making.
Conclusion:
Industry research is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that informs and guides strategic planning throughout the life of an organization. By leveraging industry research effectively, organizations can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, seize opportunities, and ultimately achieve their strategic objectives. In the following chapters, we will delve deeper into specific methodologies and best practices for conducting industry research in support of strategic planning.
Chapter 4: Gathering Primary Data for Industry Research
Primary data, which is data collected directly from original sources, is a cornerstone of effective industry research. It provides firsthand, up-to-date information that is tailored to your specific research objectives. In this chapter, we will explore the various methods and techniques for gathering primary data in industry research.
The Significance of Primary Data:
Primary data is invaluable in industry research for several reasons:
- Relevance: Primary data is collected specifically to address your research objectives, ensuring that it is highly relevant to your study.
- Accuracy: Since primary data is collected directly from the source, it tends to be more accurate and reliable than secondary data, which may be subject to interpretation or errors.
- Timeliness: Primary data provides real-time or current information, enabling you to capture the latest trends and developments in your industry.
- Control: Collecting primary data gives you control over the research process, allowing you to design surveys, questionnaires, and interviews to gather the exact information you need.
Methods for Gathering Primary Data in Industry Research:
- Surveys: Surveys are a common method for collecting primary data. They involve creating questionnaires and distributing them to a sample of respondents within the industry. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, via email, or through online survey platforms.
- Interviews: Interviews, whether structured or unstructured, provide an opportunity to gather in-depth insights directly from industry experts, key stakeholders, or decision-makers. Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, by phone, or through video conferencing.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a small, diverse group of industry participants to discuss specific topics or issues. They allow for interactive discussions and the exploration of different perspectives.
- Observations: Observational research involves systematically watching and recording behaviors, events, or processes within the industry. This method is often used in fields like ethnography or retail research.
- Experiments: In some cases, experiments may be conducted to gather primary data. This is more common in scientific or product research, where controlled experiments can be used to test hypotheses.
- Case Studies: Case studies involve in-depth examinations of specific companies, projects, or situations within the industry. They often require extensive research and analysis.
- Field Studies: Field studies involve researchers immersing themselves in the industry environment to gain firsthand experience and insights. This approach is common in social sciences and ethnographic research.
Steps in Gathering Primary Data:
- Define Research Objectives: Clearly define the research objectives and questions you want to address with primary data.
- Select Data Collection Method: Choose the most appropriate data collection method(s) based on your research objectives and available resources.
- Design Data Collection Instruments: Develop surveys, questionnaires, interview guides, or other instruments tailored to your research goals.
- Select the Sample: Determine the sample size and selection method. Ensure that your sample is representative of the industry or population you are studying.
- Collect Data: Implement your chosen data collection method, ensuring consistency and accuracy in the data gathering process.
- Analyze Data: Process and analyze the collected data using statistical or qualitative analysis techniques, depending on the nature of your research.
- Interpret Results: Interpret the data to draw meaningful conclusions and insights that address your research objectives.
- Report Findings: Present your findings in a clear, organized manner, often including tables, charts, and narratives to communicate the results effectively.
Ethical Considerations:
When gathering primary data, it's crucial to adhere to ethical guidelines, including obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring data privacy, and maintaining confidentiality.
Gathering primary data is a rigorous and valuable aspect of industry research. It allows researchers to explore specific aspects of an industry, gain insights into market trends, and contribute to evidence-based decision-making. In subsequent chapters, we will delve deeper into the specific techniques and best practices for implementing each primary data collection method.
Chapter 5: Analyzing Secondary Data in Industry Research
Secondary data analysis is a critical component of industry research, complementing primary data collection. Secondary data refers to existing data and information that has been collected by other researchers, organizations, or institutions for purposes other than your specific research objectives. In this chapter, we will explore the importance of secondary data analysis and the methods for effectively utilizing existing data sources in industry research.
The Significance of Secondary Data Analysis:
Secondary data analysis offers several advantages in industry research:
- Cost-Efficiency: It is often more cost-effective to utilize existing data than to collect new data through primary research methods.
- Time Savings: Secondary data is readily available, saving time compared to designing and conducting new data collection efforts.
- Historical Perspective: Secondary data can provide historical context, allowing researchers to track trends and changes over time.
- Comparison and Benchmarking: Existing data sources can serve as benchmarks for evaluating your own research findings.
- Broad Scope: Secondary data sources may cover a wide range of topics, including market trends, industry performance, and consumer behaviors.
Types of Secondary Data:
Secondary data can be classified into two main types:
- Internal Secondary Data: This data is generated and collected by your organization for internal purposes. Examples include sales records, customer databases, and historical performance data.
- External Secondary Data: External sources provide data collected by other organizations, institutions, or government agencies. Examples include industry reports, government statistics, academic research, and market research reports.
Methods for Analyzing Secondary Data in Industry Research:
- Data Cleaning: Before analysis, it's crucial to clean and preprocess the secondary data to address missing values, errors, and inconsistencies. Data cleaning ensures the quality and accuracy of your analysis.
- Data Exploration: Begin by exploring the secondary data to gain a comprehensive understanding of its structure and content. This step helps identify relevant variables and patterns.
- Descriptive Analysis: Use descriptive statistics and visualizations to summarize and present key findings from the secondary data. Descriptive analysis provides an initial overview of the data.
- Hypothesis Testing: If applicable, conduct hypothesis tests to examine relationships, associations, or differences within the data. This helps in answering research questions or validating hypotheses.
- Regression Analysis: Regression models can be employed to explore causal relationships and predict outcomes based on the secondary data. Regression analysis is particularly useful in predictive modeling.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the secondary data with your primary data (if applicable) or with industry benchmarks. Comparative analysis helps in identifying variances and trends.
- Time-Series Analysis: If the secondary data covers multiple time periods, time-series analysis can reveal trends and patterns over time. It is valuable for understanding historical market dynamics.
- Content Analysis: In qualitative research, content analysis can be used to examine textual data, such as reports, articles, or online content, to uncover themes and insights.
Validity and Reliability: When working with secondary data, it's essential to consider the validity and reliability of the data source. Assess the credibility, methodology, and data collection techniques used by the source to ensure that the secondary data is suitable for your research.
Ethical Considerations: Respect the terms and conditions of data usage and intellectual property rights associated with the secondary data source. Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to use and analyze the data.
Conclusion:
Secondary data analysis is a valuable tool in industry research, allowing researchers to leverage existing data sources to gain insights and make informed decisions. When properly analyzed and interpreted, secondary data can provide a wealth of information, complementing primary data collection efforts. In the following chapters, we will explore specific techniques and best practices for effectively utilizing secondary data in industry research.
Chapter 6: Competitive Analysis in Industry Research
Competitive analysis is a crucial aspect of industry research, as it provides organizations with essential insights into their rivals, their strategies, and the competitive landscape. In this chapter, we will explore the significance of competitive analysis in industry research and delve into the methodologies and best practices for conducting a thorough assessment of your competitors.
The Significance of Competitive Analysis:
Competitive analysis serves several important purposes in industry research:
- Identifying Competitors: It helps organizations identify and understand who their direct and indirect competitors are within the industry.
- Understanding Competitor Strategies: Competitive analysis reveals the strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning of competitors. This insight informs your own strategic decisions.
- Market Positioning: By evaluating where competitors stand in the market, organizations can identify opportunities for differentiation and competitive advantage.
- Risk Assessment: Analyzing competitors helps in assessing potential competitive threats and challenges that may impact your business.
- Product Development: Insights gained from competitive analysis can guide product or service development, enabling organizations to meet or surpass market expectations.
Methods for Competitive Analysis in Industry Research:
- Market Research Reports: Industry-specific market research reports often include competitive analysis sections, providing an overview of key players, their market share, and strategies.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis can be applied to competitors to assess their internal and external factors. This analysis helps identify areas of vulnerability and potential advantages.
- Competitor Profiling: Develop detailed profiles of competitors, including their history, products or services, target markets, financial performance, and key personnel.
- Product and Service Comparison: Analyze the features, quality, pricing, and value proposition of competitors' products or services compared to your own.
- Market Share Analysis: Determine the market share of each competitor within the industry to understand their relative size and influence.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Benchmark your organization's performance against that of your competitors to identify areas where you can improve and excel.
- Customer Reviews and Feedback: Examine customer reviews, feedback, and ratings for your competitors to gain insights into customer satisfaction and pain points.
- Online Presence Analysis: Evaluate competitors' online presence, including their websites, social media activities, and digital marketing strategies.
- Financial Analysis: Analyze competitors' financial statements, if available, to gain insights into their profitability, revenue growth, and financial stability.
- SWOT Analysis of Competitors: Conduct a SWOT analysis specifically for each major competitor to gain a deeper understanding of their strategic position.
Best Practices for Competitive Analysis:
- Regular Monitoring: Competitive analysis is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor the competitive landscape to stay updated on changes and developments.
- Ethical Conduct: Ensure that your competitive analysis is conducted ethically and within legal boundaries. Avoid unethical practices, such as corporate espionage or data breaches.
- Focus on Key Competitors: While it's essential to understand all competitors, prioritize your analysis on the most significant and direct competitors in your industry.
- Stay Objective: Maintain objectivity in your analysis and avoid bias. Use data and evidence to support your findings.
- Seek Different Perspectives: Encourage input from various team members and departments to gain different perspectives on competitors and their strategies.
- Use Competitive Analysis for Strategy Formulation: Translate the insights from competitive analysis into actionable strategies for your organization.
- Learn from Successes and Mistakes: Analyze both the successes and failures of competitors to learn valuable lessons and apply them to your own strategies.
Competitive analysis is a dynamic and essential component of industry research. It empowers organizations to make informed decisions, adapt to market changes, and position themselves effectively in a competitive marketplace. By understanding your competitors' strengths and weaknesses, you can develop strategies that capitalize on opportunities and mitigate threats.
Chapter 7: Industry Trends and Forecasting
Staying ahead of industry trends and accurately forecasting future developments is essential for businesses and organizations to remain competitive and make informed strategic decisions. In this chapter, we will explore the significance of tracking industry trends and the methodologies involved in forecasting future developments.
The Importance of Industry Trends:
Industry trends serve as valuable indicators of where an industry is heading and can provide several benefits:
- Strategic Planning: Understanding current and emerging trends helps organizations align their strategies with the evolving needs and preferences of their target markets.
- Innovation: Trends often highlight areas where innovation is needed. Organizations can capitalize on these opportunities to develop new products, services, or processes.
- Competitive Advantage: Being at the forefront of industry trends can give organizations a competitive edge, allowing them to differentiate themselves from rivals.
- Risk Mitigation: Anticipating negative trends or disruptions can help organizations develop risk mitigation strategies to minimize potential negative impacts.
- Market Entry: Knowledge of industry trends can inform decisions regarding market entry, expansion, or diversification into new segments or niches.
Methods for Tracking Industry Trends:
- Market Research Reports: Industry-specific reports and studies from reputable sources often provide insights into current and emerging trends within a particular sector.
- News and Publications: Regularly reading industry-related news, magazines, journals, and blogs can help organizations stay informed about the latest developments.
- Industry Associations: Many industries have associations that publish reports, organize conferences, and provide valuable information on industry trends.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms for discussions, trends, and mentions related to the industry can reveal valuable insights and emerging themes.
- Customer Feedback and Surveys: Collecting feedback from customers and conducting surveys can provide insights into their preferences, needs, and expectations.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyzing competitors' actions and strategies can offer clues about emerging trends they are capitalizing on.
Forecasting Industry Trends:
Forecasting industry trends involves making educated predictions about future developments based on existing data and historical patterns. Several forecasting methods are commonly used:
- Time-Series Analysis: This method involves analyzing historical data to identify patterns and trends over time. Time-series analysis is useful for forecasting based on past performance.
- Regression Analysis: Regression models can be used to examine the relationship between various factors and forecast future outcomes. This method is especially valuable for quantitative forecasting.
- Expert Opinion: Expert opinions and insights from industry experts, thought leaders, and analysts can provide qualitative forecasts based on their knowledge and experience.
- Scenario Planning: Scenario planning involves creating multiple possible future scenarios and analyzing the implications of each. This method is useful for preparing for various potential outcomes.
- Delphi Method: The Delphi method involves soliciting input and forecasts from a panel of experts through a series of structured surveys and feedback loops.
- New market Research: Conducting primary research, such as surveys or focus groups, can provide data for forecasting trends based on consumer preferences and behaviors.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Advanced data analytics and AI-powered algorithms can analyze large datasets and identify patterns to make predictions.
Challenges in Trend Forecasting:
Forecasting industry trends is not without challenges, including:
- Uncertainty: Future developments are inherently uncertain, and unforeseen events can disrupt even the most well-informed forecasts.
- Data Quality: The accuracy of forecasts depends on the quality and reliability of the data used for analysis.
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term: Forecasting short-term trends is generally more accurate than long-term predictions, which are subject to greater uncertainty.
- External Factors: Trends can be influenced by external factors, such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and global events, making accurate forecasting more complex.
Ethical Considerations:
When tracking and forecasting industry trends, ethical considerations include respecting data privacy, obtaining informed consent when collecting data from individuals, and adhering to ethical research practices.
In conclusion, industry trends and forecasting are essential elements of strategic planning and decision-making. By staying vigilant, collecting relevant data, and utilizing appropriate forecasting methods, organizations can better position themselves to adapt to changing market dynamics and seize opportunities for growth and innovation.
Chapter 8: Ethical Considerations in Industry Research
Ethical considerations are paramount in industry research, as they guide the responsible conduct of research and ensure the well-being of all stakeholders involved. In this chapter, we will explore the ethical principles and challenges that researchers and organizations should consider when conducting industry research.
The Importance of Ethical Conduct in Industry Research:
Ethical conduct in industry research is essential for several reasons:
- Integrity: Ethical research upholds the integrity of the research process and the credibility of the findings.
- Respect: Ethical research respects the rights, dignity, and well-being of all individuals and entities involved, including participants, colleagues, and organizations.
- Transparency: Ethical research promotes transparency by providing clear and accurate information about the research purpose, methods, and outcomes.
- Accountability: Ethical research holds researchers and organizations accountable for their actions and decisions throughout the research process.
- Trust: Ethical conduct builds trust among stakeholders, including participants, sponsors, and the public, fostering a positive research environment.
Key Ethical Considerations in Industry Research:
- Informed Consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring they understand the research's purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. Participants should have the freedom to withdraw from the study at any time without consequences.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Researchers must protect the privacy of individuals and organizations involved in the research. Data should be anonymized and stored securely to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: Researchers are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data collection, analysis, and reporting. Data should not be manipulated or misrepresented.
- Conflict of Interest: Researchers should disclose any potential conflicts of interest that could compromise the integrity or objectivity of the research. This includes financial interests, affiliations, or biases.
- Respect for Diversity: Researchers should respect and value diversity among participants and stakeholders, including differences in culture, gender, age, and background.
- Beneficence and Non-Maleficence: Researchers should prioritize the well-being of participants and stakeholders, striving to maximize benefits while minimizing harm.
- Transparency and Honesty: Researchers should provide clear, accurate, and honest information about the research process, methods, and findings. Any limitations or uncertainties should be communicated transparently.
- Publication Ethics: Researchers should follow ethical guidelines when publishing research results, including proper citation of sources, avoiding plagiarism, and disclosing conflicts of interest.
Challenges in Ethical Conduct in Industry Research:
- Data Privacy: As industry research often involves collecting sensitive data, researchers must navigate data privacy regulations and ensure compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA.
- Big Data and AI: The use of big data and artificial intelligence in industry research raises ethical concerns related to data security, algorithm bias, and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Confidentiality Agreements: Researchers may be bound by confidentiality agreements that limit their ability to share research findings or disclose certain information.
- Balancing Stakeholder Interests: Researchers must balance the interests of various stakeholders, including participants, organizations, funders, and the public, which can sometimes be conflicting.
- International Research: Conducting research in multiple countries introduces additional ethical complexities related to cultural differences, legal requirements, and informed consent procedures.
Codes of Ethics and Guidelines:
Professional organizations and institutions often provide codes of ethics and guidelines specific to industry research. Researchers and organizations should familiarize themselves with these codes and adhere to them.
Conclusion:
Ethical conduct is the foundation of responsible and credible industry research. By prioritizing ethical principles throughout the research process, researchers and organizations can uphold the integrity of their work, protect the rights of participants and stakeholders, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and innovation in their respective industries. Ethical research not only ensures compliance with legal and professional standards but also fosters trust and respect within the research community and society at large.
Chapter 9: Emerging Technologies in Industry Research
The landscape of industry research is continually evolving, thanks to the integration of emerging technologies. These technologies are reshaping the way data is collected, analyzed, and utilized in industry research. In this chapter, we will explore the impact of emerging technologies on industry research and the opportunities they present for organizations.
The Role of Emerging Technologies:
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing industry research in several ways:
- Data Collection: Advanced sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and wearables are enabling the collection of vast amounts of real-time data from various sources.
- Data Analysis: Machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics tools are improving the speed and accuracy of data analysis, uncovering insights that were previously challenging to discern.
- Automation: Robotic process automation (RPA) and cognitive automation are automating repetitive tasks in data collection, analysis, and reporting, saving time and reducing errors.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive modeling and algorithms are helping organizations forecast future trends, market dynamics, and consumer behaviors with greater precision.
- Data Visualization: Advanced data visualization techniques and tools are making it easier to communicate complex research findings to diverse audiences.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Industry Research:
- Improved Data Quality: Emerging technologies enhance data collection accuracy and reduce the likelihood of human errors, resulting in higher data quality.
- Faster Insights: Advanced analytics and AI algorithms can quickly process large datasets, providing insights in real-time or near-real-time.
- Enhanced Personalization: AI-driven analytics enable organizations to personalize research and marketing efforts based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation and AI-driven processes can reduce research costs by streamlining data collection and analysis.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that harness emerging technologies effectively gain a competitive edge by being more agile and data-driven.
Examples of Emerging Technologies in Industry Research:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is used for natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and predictive analytics, enabling deeper and more automated data analysis.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms can uncover hidden patterns, classify data, and make predictions based on historical data.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology enhances data security and transparency, making it useful for verifying the authenticity of data sources.
- IoT Sensors: IoT sensors collect real-time data from physical objects, enabling organizations to monitor and analyze operational processes and supply chains.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies can be used in immersive market research experiences, such as product testing and virtual store simulations.
- Big Data Analytics: Advanced big data analytics tools can process and analyze massive datasets, identifying trends and insights that might have been missed with traditional methods.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA automates repetitive tasks in data processing and reporting, reducing human errors and speeding up research processes.
Challenges in Adopting Emerging Technologies:
- Data Privacy and Security: With the increased use of technology comes the responsibility of safeguarding sensitive data and complying with data privacy regulations.
- Skills Gap: Adopting emerging technologies often requires specialized skills and expertise, which may not be readily available in organizations.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating new technologies with existing systems can be complex and require careful planning.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of AI and automation may raise ethical questions, especially when it comes to bias in algorithms or the potential for job displacement.
Future Prospects:
As technology continues to advance, industry research will likely see further integration of emerging technologies. Organizations that embrace these technologies and adapt their research practices are well-positioned to navigate the rapidly evolving business landscape and gain a competitive advantage.
In the following years, it is expected that emerging technologies will continue to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and depth of industry research, opening new possibilities for innovation and growth. Researchers and organizations should remain vigilant in monitoring technological developments and consider how they can leverage these tools to improve their research capabilities.
Chapter 10: The Future of Industry Research: Trends and Challenges
The future of industry research promises both exciting opportunities and significant challenges as the field continues to evolve. In this concluding chapter, we will explore the anticipated trends and emerging challenges that will shape the landscape of industry research in the years to come.
Anticipated Trends in Industry Research:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will play an increasingly prominent role in industry research, enabling more sophisticated data analysis, predictive modeling, and automation of research processes.
- Big Data Integration: The integration of big data from various sources, including IoT devices, social media, and online market intelligence platforms, will become standard practice, providing richer and more comprehensive datasets for analysis.
- Blockchain for Data Security: Blockchain technology will be employed to enhance data security, authentication, and the verification of data sources, particularly in industries where data integrity is critical.
- Real-Time Data: The demand for real-time data will grow, necessitating the development of faster data collection and analysis methods to support agile decision-making.
- Ethical and Responsible Research: Ethical considerations and responsible research practices will remain at the forefront, with a heightened focus on data privacy, transparency, and fairness in AI algorithms.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: VR and AR technologies will find broader applications in industry research, enabling immersive experiences for consumer behavior analysis, product testing, and market simulations.
- Cross-Industry Collaboration: Collaborative research efforts between industries and sectors will become more common as organizations seek to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Sustainability and ESG Research: Research on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors will gain prominence as sustainability becomes a key consideration for investors, consumers, and regulators.
Emerging Challenges in Industry Research:
- Data Privacy and Security: As the volume of data collected and analyzed grows, maintaining data privacy and security will remain a significant challenge, particularly in the face of evolving regulations.
- Ethical AI: Addressing bias, fairness, and transparency in AI algorithms will be an ongoing challenge to ensure that AI-driven research is conducted responsibly.
- Interoperability: Integrating data from diverse sources and systems will require efforts to improve interoperability and data standardization.
- Skills Gap: The demand for professionals with expertise in emerging technologies, data science, and analytics will outpace the availability of skilled talent, creating a skills gap.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating a complex regulatory environment, especially in areas like data protection and AI ethics, will require organizations to stay informed and compliant.
- Data Overload: Managing and extracting meaningful insights from the ever-growing volume of data will be a persistent challenge, necessitating advanced data management and analysis techniques.
- Sustainability Concerns: Organizations will need to address sustainability challenges, including the environmental impact of data centers and the ethical implications of data collection.
- Globalization and Cultural Sensitivity: Conducting research in a globalized world requires sensitivity to cultural differences, regulatory variations, and local market dynamics.
Conclusion:
The future of industry research is shaped by the rapid advancement of technology, the growing importance of data-driven insights, and the evolving expectations of stakeholders. As industry research continues to evolve, organizations and researchers must embrace emerging technologies, adhere to ethical principles, and navigate the challenges that come with an ever-changing research landscape.
Successful industry research in the future will require a multidisciplinary approach, a commitment to ethical conduct, and a readiness to adapt to new technologies and methodologies. By staying informed, fostering collaboration, and embracing responsible research practices, organizations and researchers can harness the full potential of industry research to drive innovation, make informed decisions, and stay competitive in dynamic markets.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.