Market Reports
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Reports
Chapter 2: Types of Market Reports
Chapter 3: Components of a Market Report
Chapter 4: Market Report Writing Essentials
Chapter 5: Interpreting Market Data
Chapter 6: Market Segmentation and Targeting
Chapter 7: Competitor Analysis
Chapter 8: Regulatory and Legal Considerations in Market Reporting
Chapter 9: Practical Applications of Market Reports
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Market Reports
Appendices: Additional Resources and Templates
This 9-chapter guide will provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of market reports, from their types and components to the practical applications that drive business success. It will equip them with the knowledge and tools needed to harness the power of market reports effectively in their decision-making processes.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Market Reports
In the fast-paced world of business and commerce, staying informed about market dynamics and trends is essential for making informed decisions. Market reports play a pivotal role in this regard, serving as invaluable tools that provide insights into various aspects of markets, industries, and consumer behavior. This chapter lays the foundation for our journey into the realm of market reports, exploring what they are, why they are important, and the overarching purpose of this comprehensive guide.
1.1 Defining Market Reports
Market research reports, also known as business reports or
1.2 Why Are Market Reports Important?
Market reports hold immense importance for various stakeholders across industries and sectors. Here's why they are considered indispensable:
Informed Decision-Making:
- Market reports provide decision-makers with vital information to make informed choices regarding investments, product development, marketing strategies, and more.
Competitive Advantage:
- They empower businesses with a competitive edge by offering insights into competitors' strategies, market gaps, and emerging trends.
Risk Mitigation:
- Understanding market dynamics helps in risk assessment and management, enabling companies to anticipate and prepare for market fluctuations.
Investment Opportunities:
- Investors rely on market reports to identify promising sectors and industries for potential investments.
Government Policy Formulation:
- Governments use market reports to shape policies, promote economic growth, and regulate industries effectively.
Academic and Research Purposes:
- Researchers and academia leverage market reports for studies, data analysis, and trend exploration.
1.3 The Scope and Purpose of This Guide
As you delve deeper into this guide, you will gain comprehensive knowledge about market reports, from the various types available to the components that make up a well-structured report. We will explore the intricacies of conducting market research, writing effective market reports, interpreting data, and applying market insights to real-world scenarios.
By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the skills and understanding necessary to harness the power of market reports for strategic decision-making, competitive advantage, and business success. Whether you are a business professional, entrepreneur, investor, or researcher, the insights gained from this guide will prove invaluable in your pursuit of excellence in your respective endeavors. So, let's embark on this journey to master the art of market reports and unlock their potential to drive growth and innovation in your domain.
Chapter 2: Types of Market Reports
Market reports come in various forms, each tailored to address specific aspects of a market, industry, or consumer behavior. Understanding the different types of market reports is crucial as it enables you to choose the right report that aligns with your specific objectives and information needs. In this chapter, we explore the diverse landscape of market reports, from industry-specific to consumer-focused, and discuss the pros and cons of each.
2.1 Industry Reports
Industry reports provide an in-depth analysis of a particular industry or sector. These reports focus on understanding the industry's structure, key players, market size, growth prospects, and challenges. Here are some key features:
Pros:
- Comprehensive Insight: Industry reports offer a holistic view of the entire sector, including market trends, regulatory developments, and competitive landscapes.
- Strategic Planning: Businesses use industry reports to formulate long-term strategies, identify growth opportunities, and assess market risks.
Cons:
- Generic Information: Some industry reports may contain generic data that does not cater to a specific niche or sub-sector.
- Limited Customization: These reports are pre-packaged and may not always address the unique needs of every organization.
2.2 Competitive Analysis Reports
Competitive analysis reports are centered around understanding the competitive landscape within a specific market. They delve deep into the strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positions of key players.
Pros:
- Strategic Insights: Competitive analysis reports help businesses benchmark themselves against competitors, enabling them to refine their strategies.
- Market Entry: These reports assist new entrants in understanding market dynamics and identifying opportunities to compete effectively.
Cons:
- Data Availability: Access to accurate and up-to-date data on competitors can be challenging, especially for private companies.
- Narrow Focus: These reports may overlook broader market trends, potentially leading to missed opportunities.
2.3 Consumer Behavior Reports
Consumer behavior reports aim to unravel the preferences, habits, and buying patterns of consumers. They are essential for businesses seeking to tailor their products and marketing strategies to meet consumer demands.
Pros:
- Customer-Centric Approach: These reports enable businesses to create products and marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience.
- Product Development: Understanding consumer behavior can lead to the development of products that better meet market needs.
Cons:
- Changing Landscape: Consumer preferences can change rapidly, making it challenging to rely solely on historical data.
- Interpretation Complexity: Analyzing consumer behavior data requires expertise in psychology, sociology, and market research.
2.4 Market Entry and Expansion Reports
Market entry and expansion reports provide guidance to businesses planning to enter new markets or expand their presence in existing ones. They offer insights into market readiness, potential risks, and entry strategies.
Pros:
- Informed Expansion: These reports help businesses make informed decisions about where and how to expand, minimizing risks.
- Entry Strategies: Market entry reports offer recommendations on the most suitable entry methods, such as partnerships, acquisitions, or organic growth.
Cons:
- Market Uncertainty: Market entry reports can't eliminate all uncertainties, and unforeseen challenges may still arise.
- Costly Investment: Preparing and acquiring comprehensive market entry reports can be expensive.
2.5 Economic and Macroeconomic Reports
Economic and macroeconomic reports provide a broader perspective by analyzing the economic conditions of a region, country, or global market. They offer insights into factors like inflation, GDP growth, interest rates, and fiscal policies.
Pros:
- Holistic View: These reports help businesses understand the macroeconomic factors influencing their operations.
- Risk Assessment: By monitoring economic indicators, organizations can anticipate potential economic downturns.
Cons:
- Limited Industry Focus: Economic reports may not provide industry-specific insights, which are crucial for some businesses.
- Lagging Indicators: Economic data often reflects past events and may not be predictive of future trends.
2.6 Customized Reports
Customized reports are tailored to meet the specific needs of an organization. They can combine elements of the previously mentioned report types to provide a personalized analysis.
Pros:
- Tailored Insights: Customized reports address the unique requirements and objectives of a business.
- Flexibility: Organizations have control over the scope, depth, and format of the report.
Cons:
- Costly and Time-Consuming: Customized reports can be more expensive and time-consuming to produce compared to pre-packaged reports.
- Expertise Required: Developing a customized report may necessitate specialized market research expertise.
Understanding the various types of market reports allows businesses and decision-makers to select the most appropriate report for their specific needs. In the subsequent chapters of this guide, we will delve deeper into the components and methodologies involved in creating these reports and explore how to extract valuable insights from them.
Chapter 3: Components of a Market Report
A well-structured market report consists of several essential components that collectively provide a comprehensive and clear understanding of the market, industry, or consumer behavior being analyzed. In this chapter, we will explore these key components and their significance in creating a valuable market report.
3.1 Executive Summary
The executive summary is a concise and compelling overview of the entire market report. It serves as a snapshot for busy executives and decision-makers, providing them with a quick understanding of the report's main findings and recommendations. Key elements of an effective executive summary include:
- Report Purpose: A brief statement of the report's objective and scope.
- Major Findings: Summarized insights and significant data points.
- Recommendations: Clear and actionable suggestions based on the report's findings.
- Key Metrics: Highlighted statistics or figures that are particularly important.
The executive summary should entice readers to explore the report further and serve as a reference point for quick decision-making.
3.2 Table of Contents
The table of contents is a roadmap that outlines the structure and organization of the market report. It provides readers with a clear outline of what to expect and facilitates easy navigation. The table of contents typically includes headings and page numbers for each section and subsection.
3.3 Methodology
The methodology section details the approach used to gather and analyze data for the report. It is essential for establishing the report's credibility and transparency. Key elements of the methodology section include:
- Data Sources: A list of primary and secondary data sources used.
- Data Collection Methods: An explanation of how data was collected, including surveys, interviews, observations, or data mining.
- Sampling Techniques: Details about the sampling method employed if applicable.
- Data Analysis Tools: Mention of any software or statistical tools used for data analysis.
- Limitations: A candid discussion of the limitations of the methodology and potential sources of bias.
A robust methodology section allows readers to assess the validity of the report's findings and the rigor of the research process.
3.4 Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the report by providing context and background information. Key elements of the introduction include:
- Problem Statement: A clear definition of the problem or question the report aims to address.
- Objectives: Stated goals and objectives of the report.
- Scope: The boundaries of the report, specifying what is and isn't covered.
- Significance: Why the report's subject matter is important and relevant.
The introduction helps readers understand the purpose and relevance of the report, making it easier for them to engage with the content.
3.5 Market Overview
The market overview section provides a broad yet concise description of the market or industry being analyzed. Key elements of the market overview include:
- Market Definition: A clear definition of the market, including its boundaries and segments.
- Market Size and Growth: Current market size, historical growth, and future growth projections.
- Market Trends: Notable trends, patterns, and developments in the market.
- Market Dynamics: Factors influencing supply, demand, and competition within the market.
This section sets the stage for the more detailed analysis that follows and helps readers establish a foundational understanding of the market.
3.6 Findings and Analysis
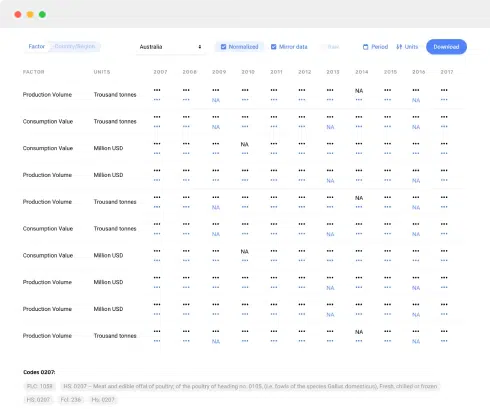
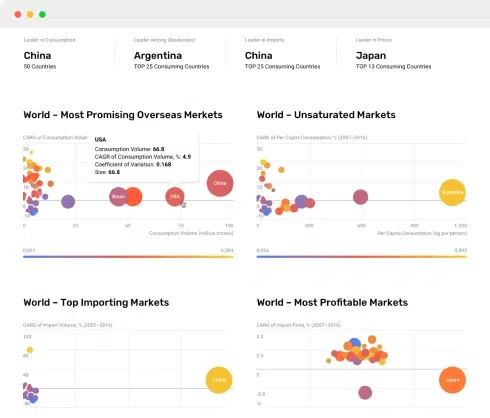
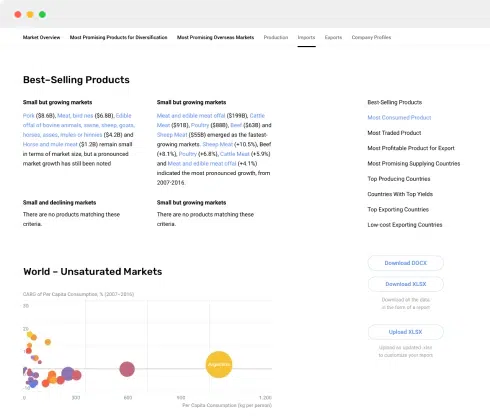
The findings and analysis section forms the core of the market report. It presents the results of data analysis, trends, and insights gleaned from research. Key elements of this section include:
- Data Presentation: Charts, graphs, tables, and visuals that illustrate key data points.
- Interpretation: Analysis and interpretation of the data, explaining its significance.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparisons with historical data, benchmarks, or competitors.
- Insights and Patterns: Identification of key insights, trends, and patterns in the data.
This section should be thorough, logical, and well-structured, guiding readers through the analysis and helping them draw their conclusions.
3.7 Recommendations
The recommendations section provides actionable suggestions and strategic guidance based on the report's findings. It answers the question, "What should be done next?" Key elements of this section include:
- Strategic Actions: Clear, specific recommendations for businesses or organizations.
- Implementation Steps: Practical steps to execute the recommendations.
- Risk Assessment: Consideration of potential risks and challenges in implementing the recommendations.
The recommendations section is where the report's value becomes tangible, as it guides decision-makers toward informed actions.
3.8 Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the key takeaways from the report, reiterates its significance, and reinforces the main findings and recommendations. It serves as a final reflection on the report's objectives and outcomes.
3.9 References
The references section lists all the sources, data, and materials cited or referenced in the report. Proper citation is crucial for transparency and credibility.
3.10 Appendices
The appendices contain additional information that supports the report, such as supplementary data, detailed survey results, or technical details about the methodology. Appendices are useful for readers who wish to delve deeper into the report's content.
A well-structured market report incorporates these components seamlessly to deliver a comprehensive, informative, and actionable document that aids decision-making, strategy development, and market understanding. In the subsequent chapters of this guide, we will explore each of these components in more detail, offering practical tips and best practices for creating effective market reports.
Chapter 4: Market Report Writing Essentials
Once you've conducted thorough market research, the next crucial step is to transform your findings into a well-structured and informative market report. In this chapter, we will explore the essential components and best practices for writing an effective market report with intelligence tools.
4.1 Clarity and Conciseness
Clarity and conciseness are the cornerstones of effective report writing. Ensure that your writing is clear, straightforward, and free from jargon or unnecessary complexity. Use plain language that can be easily understood by a broad audience, including those who may not be experts in the field.
4.2 Structure and Organization
A well-organized structure is essential for guiding readers through your market report. Common structural elements include:
- Title Page: The report's title, authorship, date, and any relevant affiliations.
- Table of Contents: An outline of the report's sections and page numbers for easy navigation.
- Executive Summary: A concise summary of the report's key findings and recommendations.
- Introduction: An introduction that provides context, objectives, and the scope of the report.
- Methodology: An explanation of the research methods and data sources used.
- Market Overview: A section providing an overview of the market or industry being studied.
- Findings and Analysis: The core of the report, presenting research findings, analysis, and insights.
- Recommendations: Actionable suggestions based on the research findings.
- Conclusion: A summary of the report's key takeaways and significance.
- References: A list of sources and references used in the report.
- Appendices: Supplementary materials, such as additional data or detailed charts and graphs.
Adhering to this structure ensures that your report flows logically and is easy to navigate.
4.3 Data Presentation
Effective data presentation is crucial in conveying your research findings. Use a variety of data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, tables, and infographics, to make complex information more accessible. Ensure that visuals are labeled, titled, and referenced appropriately.
4.4 Use of Language
Maintain a consistent and professional tone throughout your report. Avoid using overly technical language or jargon that may confuse readers. Use active voice and straightforward sentence structures to enhance readability.
4.5 Citation and Referencing
Accurate citation and referencing are vital for maintaining the credibility of your report. Clearly attribute all data, quotes, and ideas to their sources using a recognized citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Ensure that your references are complete and consistent.
4.6 Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion section should provide a concise summary of the report's main findings and their implications. It should reinforce the significance of the research and set the stage for the recommendations.
In the recommendations section, offer actionable suggestions based on your research. Recommendations should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Explain how each recommendation addresses the findings and contributes to the report's objectives.
4.7 Review and Editing
Thoroughly review and edit your report for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. It's often beneficial to have someone else review the report as well to catch any overlooked mistakes or ambiguities.
4.8 Executive Summary
The executive summary, though mentioned earlier, deserves special attention. It is often the first part of the report that decision-makers read. Ensure that your executive summary effectively captures the essence of the report, highlighting key findings and recommendations concisely.
4.9 Visual Appeal
Consider the visual appeal of your report. Use a consistent and professional design with appropriate fonts, colors, and formatting. Well-designed reports are more likely to engage readers.
4.10 Tailored Content
Keep your audience in mind when writing your report. Tailor the content to address the specific needs and interests of your target readers. Consider the level of detail required for different audiences, such as executives, investors, or industry experts.
4.11 Executive Briefing
In addition to the full report, prepare an executive briefing or summary document that distills the report's key points into a concise format. This is especially helpful for busy decision-makers who may not have the time to read the entire report.
4.12 Peer Review
If possible, seek peer review or feedback from subject matter experts or colleagues with expertise in the field. External input can provide valuable insights and help improve the report's quality.
By following these writing essentials, you can create a market report that effectively communicates your research findings and recommendations to your target audience. A well-written report not only informs but also empowers decision-makers to make informed choices and strategies based on the insights you've uncovered.
Chapter 5: Interpreting Market Data
Interpreting market data is a critical step in transforming raw information into meaningful insights that can drive strategic decisions. In this chapter, we will explore various techniques and considerations for effectively interpreting market data.
5.1 Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis involves a systematic examination of data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. Depending on the nature of the data, different techniques can be applied:
- Descriptive Analysis: Summarizing data using statistics, such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation, to gain an overview of central tendencies and variability.
- Inferential Analysis: Making predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data, often using techniques like hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
- Regression Analysis: Assessing the relationship between variables, with techniques like linear regression for continuous data or logistic regression for categorical data.
- Cluster Analysis: Grouping data points into clusters based on similarities.
- Factor Analysis: Identifying underlying factors or dimensions that explain the variance in the data.
- Time Series Analysis: Analyzing data collected over time to identify trends, seasonality, and cyclic patterns.
- Textual Analysis: Applying natural language processing techniques to analyze textual data, such as customer reviews or social media sentiment.
The choice of analysis technique depends on the research objectives and the type of data available.
5.2 Identifying Key Insights
While analyzing data, focus on identifying key insights that provide answers to the research questions or objectives. Key insights may include:
- Market Trends: Recognizing patterns or shifts in market behavior over time.
- Consumer Behavior: Understanding consumer preferences, buying patterns, and decision-making processes.
- Competitor Strategies: Identifying strategies and tactics used by competitors.
- Market Segmentation: Uncovering distinct market segments and their characteristics.
- Emerging Opportunities: Detecting emerging market niches or growth prospects.
- Risk Factors: Highlighting potential risks or challenges in the market.
Effective data interpretation involves distilling complex information into clear, actionable insights that can inform decision-making.
5.3 Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool for interpreting and communicating market data. Visual representations, such as charts, graphs, heatmaps, and infographics, can make complex data more accessible and understandable. Consider the following tips for effective data visualization:
- Choose the most appropriate type of visualization for your data (e.g., bar charts, line graphs, pie charts).
- Ensure that visuals are labeled, titled, and easy to interpret.
- Use color coding and legends effectively to convey information.
- Avoid clutter and excessive detail in visuals.
- Provide context and explanations for visuals in the report.
5.4 Cross-Verification
Cross-verification of data and insights is a crucial step in data interpretation. Ensure that findings are consistent across different data sources, methods, and analysis techniques. Inconsistencies or discrepancies should be investigated and resolved to maintain the accuracy and reliability of your insights.
5.5 Data Limitations and Assumptions
Acknowledge and communicate the limitations and assumptions of your data and analysis. No dataset is perfect, and understanding the constraints and potential sources of bias is essential for decision-makers to interpret findings correctly.
5.6 Scenario Analysis
Consider conducting scenario analysis to explore different possible outcomes or future scenarios based on your data and insights. This can help decision-makers understand the range of possibilities and make more informed choices in uncertain environments.
5.7 Collaborative Interpretation
Interpreting market data is often a collaborative effort involving multiple stakeholders, including subject matter experts, analysts, and decision-makers. Encourage open discussions and knowledge sharing to gain diverse perspectives and enhance the quality of interpretation.
5.8 Continuous Monitoring
Market data interpretation is not a one-time task. Markets evolve, and new data becomes available. Establish processes for continuous monitoring and analysis to keep your insights up to date and relevant.
5.9 Actionable Recommendations
Ultimately, the goal of interpreting market data is to generate actionable recommendations. Ensure that your insights are translated into practical, measurable, and achievable recommendations that align with the objectives of your market report.
Interpreting market data is both a science and an art. It requires analytical rigor, critical thinking, and the ability to extract meaningful insights from complex information. By following these techniques and considerations, you can provide decision-makers with the valuable insights they need to make informed and strategic choices.
Chapter 6: Market Segmentation and Targeting
Market segmentation and targeting are essential strategies for businesses seeking to understand and reach their customers effectively. In this chapter, we will delve into the concepts of market segmentation, the importance of segmentation, and how to identify and target specific market segments.
6.1 Understanding Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broader market into smaller, distinct groups or segments based on shared characteristics, needs, behaviors, or preferences. Segmentation helps businesses tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of different customer groups.
6.2 The Importance of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is vital for several reasons:
- Enhanced Customer Understanding: It allows businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their diverse customer base.
- Targeted Marketing: Segmentation enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups.
- Product Customization: By understanding the unique needs of different segments, businesses can customize their products or services to cater to those needs.
- Resource Optimization: Segmentation helps allocate resources more efficiently by focusing efforts on the most promising segments.
- Competitive Advantage: Tailoring offerings to specific segments can lead to a competitive edge by addressing unmet needs or preferences.
- Market Expansion: Identifying new, untapped segments can open opportunities for growth and market expansion.
6.3 Market Segmentation Criteria
Market segmentation can be based on various criteria, including:
- Demographics: Characteristics such as age, gender, income, education, and family size.
- Geographics: Geographic location, such as region, country, city, or climate.
- Psychographics: Psychological and lifestyle factors, including values, interests, opinions, and behaviors.
- Behavioral: Customer behaviors, such as purchasing habits, brand loyalty, product usage, or buying frequency.
- Firmographic: B2B segmentation based on characteristics like industry, company size, and revenue.
- Technographic: B2B segmentation based on technology adoption and preferences.
- Needs and Benefits: Segmentation based on specific needs or benefits sought by customers.
6.4 Segmenting B2B and B2C Markets
Segmentation strategies can differ for business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) markets. B2C segmentation often focuses on individual consumers, while B2B segmentation considers organizations as customers. B2B segmentation may involve factors like industry, company size, procurement processes, and decision-making units within organizations.
6.5 Targeting Specific Segments
Once segments are identified, businesses must decide which segments to target. Targeting involves selecting one or more segments that align with the organization's objectives and resources. Common targeting strategies include:
- Undifferentiated Targeting: Serving the entire market with a single marketing mix.
- Differentiated Targeting: Developing distinct marketing strategies for multiple segments.
- Niche Targeting: Concentrating on a small, specialized segment.
- Micromarketing: Customizing offerings for individual customers or very small segments.
The choice of targeting strategy depends on factors like market size, competitiveness, and the organization's capabilities.
6.6 Positioning
Positioning is the process of establishing a distinct and desirable place for a product or brand in the minds of the target audience within a segment. Effective positioning defines how the product or brand is perceived compared to competitors. It involves crafting a unique value proposition that resonates with the chosen segment.
6.7 Continuous Assessment
Market segmentation and targeting are not static processes. Market dynamics change, and customer preferences evolve over time. Continuous assessment and adjustment of segmentation and targeting strategies are necessary to remain competitive and relevant in the market.
6.8 Case Studies and Examples
Throughout this chapter, we will explore real-world case studies and examples to illustrate the practical application of market segmentation and targeting strategies in various industries and contexts.
Market segmentation and targeting are essential components of a successful marketing strategy. By understanding your customers, identifying distinct segments, and tailoring your offerings to meet their needs, you can build stronger customer relationships, increase market share, and drive business growth.
Chapter 7: Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis is a fundamental aspect of market research and strategic planning. Understanding your competitors' strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positions is crucial for making informed business decisions. In this chapter, we will explore the significance of competitor analysis and the steps involved in conducting a comprehensive assessment of your competitors.
7.1 The Importance of Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis provides several key benefits for businesses:
- Strategic Planning: It helps identify opportunities and threats in the market, informing strategic decisions.
- Differentiation: Understanding competitors allows businesses to differentiate their products or services effectively.
- Market Positioning: It aids in positioning your brand in a way that highlights your strengths relative to competitors.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying competitor actions or market shifts can help mitigate risks.
- Innovation: Insights into competitors' weaknesses can drive innovation and product development.
- Resource Allocation: It assists in allocating resources effectively by focusing on areas where you can outperform competitors.
- Market Entry: For new entrants, competitor analysis is vital for understanding the competitive landscape.
7.2 Steps in Competitor Analysis
Effective competitor analysis involves a systematic approach. Here are the steps to conducting a thorough analysis:
7.2.1 Identify Competitors
Start by identifying your direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors offer similar products or services to the same target market. Indirect competitors may offer different products or serve slightly different markets but still impact your business.
7.2.2 Gather Information
Collect data and information about your competitors. Sources of information may include:
- Publicly Available Data: Websites, annual reports, press releases, and news articles.
- Customer Feedback: Reviews, testimonials, and social media comments.
- Industry Reports: Market research reports and industry publications.
- Competitor Websites: Analyze their products, pricing, and messaging.
7.2.3 SWOT Analysis
Conduct a SWOT analysis for each competitor:
- Strengths: Identify their advantages and what they do well.
- Weaknesses: Discover areas where they may be vulnerable.
- Opportunities: Examine market trends or gaps they can exploit.
- Threats: Recognize potential challenges or risks they face.
7.2.4 Market Positioning
Determine how competitors position themselves in the market. Analyze their brand image, value proposition, and messaging. Understand what sets them apart from others.
7.2.5 Pricing Strategies
Examine competitors' pricing strategies, including pricing models, discounts, and promotions. Understand their pricing relative to the perceived value of their products or services.
7.2.6 Product and Service Offerings
Analyze competitors' product or service offerings. Consider features, quality, and how they meet customer needs. Identify any gaps or opportunities for differentiation.
7.2.7 Marketing and Sales Channels
Assess competitors' marketing and sales channels. Examine their advertising, digital marketing, distribution networks, and sales processes.
7.2.8 Customer Base
Understand who their customers are and their customer retention strategies. Analyze customer reviews and feedback to gauge customer satisfaction.
7.2.9 Financial Health
Review competitors' financial statements, if available. Look at revenue, profit margins, and growth trends. Assess their financial stability.
7.2.10 Competitive Advantages
Identify what gives each competitor a competitive edge. Is it their technology, customer service, brand reputation, or something else?
7.2.11 Future Plans
Examine any publicly stated plans or strategies of competitors, such as expansion plans, product launches, or acquisitions.
7.3 Competitive Benchmarking
Benchmark your own business against competitors. Compare key performance metrics, such as market share, customer satisfaction, and financial performance, to gain insights into areas where you can improve.
7.4 Ethical Considerations
While conducting competitor analysis, be mindful of ethical considerations. Avoid unethical practices like industrial espionage or spreading false information about competitors. Ethical competitor analysis respects legal and ethical boundaries.
7.5 Continuous Monitoring
Competitor analysis is not a one-time task. The competitive landscape evolves, and competitors adapt. Regularly monitor competitors and adjust your strategies accordingly.
7.6 Case Studies and Examples
Throughout this chapter, we will explore real-world case studies and examples to illustrate effective competitor analysis strategies and their impact on business decisions.
Competitor analysis is a continuous process that informs your business strategy and helps you stay competitive in a dynamic market. By understanding your competitors' strengths, weaknesses, and strategies, you can identify opportunities for growth and make informed decisions that give your business a competitive edge.
Chapter 8: Regulatory and Legal Considerations in Market Reporting
Market reporting often involves the collection and dissemination of information that can have significant legal and regulatory implications. In this chapter, we will explore the crucial regulatory and legal considerations that businesses and individuals should be aware of when conducting market research and producing market reports.
8.1 Regulatory Framework
Understanding the regulatory framework governing market reporting is essential. Regulations vary by region and industry but generally focus on:
- Data Privacy: Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States govern the collection and handling of personal data.
- Securities Regulations: Regulations like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rules in the U.S. mandate the disclosure of material information by publicly traded companies.
- Consumer Protection: Regulations protect consumers from false advertising, deceptive practices, and fraud.
- Antitrust Laws: Laws prohibit anticompetitive behavior and unfair trade practices that could harm competition and consumers.
- Intellectual Property: Intellectual property laws protect trademarks, copyrights, and patents related to market reports, data, and research.
8.2 Data Privacy and Consent
Respecting data privacy laws is crucial. Ensure that you have appropriate consent to collect, store, and use personal data. Anonymize or pseudonymize data when necessary to protect individuals' identities.
8.3 Accuracy and Truthfulness
Market reports must be accurate and truthful. Misrepresenting data or making false claims can lead to legal consequences and damage your reputation.
8.4 Copyright and Intellectual Property
Respect copyright and intellectual property rights. Properly attribute and obtain permissions for any content, images, or data that you use in your reports. Plagiarism can lead to legal disputes.
8.5 Securities Regulations
If your market reports involve publicly traded companies, be aware of securities regulations that require the disclosure of material information. Misreporting or insider trading can result in severe penalties.
8.6 Insider Trading
Insider trading, or trading on non-public information, is illegal in many jurisdictions. Be cautious about sharing or acting on material non-public information when producing or distributing market reports.
8.7 Antitrust and Fair Competition
Avoid engaging in anticompetitive behavior or unfair trade practices that harm competition. Unlawful collusion, price-fixing, or market manipulation can lead to antitrust investigations and penalties.
8.8 Consumer Protection Laws
Market reports should not engage in deceptive practices or false advertising. Misleading consumers can lead to legal action and damage your brand's reputation.
8.9 Compliance Programs
Establish compliance programs within your organization to ensure that market reporting activities align with relevant regulations and laws. This may include training, internal audits, and legal counsel.
8.10 International Considerations
If your market reports have an international audience or include data from multiple countries, be aware of cross-border data transfer regulations and consider the implications of different legal frameworks.
8.11 Legal Counsel
Consult legal counsel with expertise in market reporting and relevant regulations. They can provide guidance on compliance and help mitigate legal risks.
8.12 Document Retention
Maintain records of your market research and reporting activities. Document your data sources, methodologies, and any legal and compliance steps taken. This documentation can be valuable in case of legal inquiries.
8.13 Ethical Considerations
Beyond legal requirements, adhere to ethical principles in market reporting. Transparency, honesty, and integrity are essential for maintaining trust with stakeholders.
8.14 Data Security
Protect sensitive data with robust cybersecurity measures. Data breaches can result in legal consequences and harm your organization's reputation.
8.15 Case Studies and Examples
Throughout this chapter, we will examine real-world case studies and examples of legal and regulatory issues related to market reporting to highlight the importance of compliance and ethical conduct.
Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape in market reporting is complex but essential. Compliance not only mitigates legal risks but also helps build trust with customers, investors, and stakeholders. By understanding and adhering to the relevant regulations and legal considerations, you can produce market reports that are not only valuable but also compliant and trustworthy.
Chapter 9: Practical Applications of Market Reports
Market reports are valuable tools that offer insights and guidance for a wide range of practical applications across various industries and sectors. In this chapter, we will explore some of the most common and impactful practical applications of market reports.
9.1 Strategic Decision-Making
One of the primary applications of market reports is aiding strategic decision-making. Businesses use market reports to:
- Identify Growth Opportunities: Market reports help businesses identify new markets, emerging trends, and growth opportunities.
- Competitive Analysis: Reports provide insights into competitors' strategies, strengths, and weaknesses, informing competitive positioning.
- Risk Assessment: Reports help assess market risks, regulatory changes, and potential threats to business operations.
- Resource Allocation: Businesses allocate resources more effectively based on market insights and opportunities.
9.2 Market Entry and Expansion
Market reports are crucial for companies looking to enter new markets or expand their existing footprint. These reports assist by:
- Market Assessment: Evaluating the attractiveness and potential of a market.
- Market Sizing: Determining the size and growth potential of a market segment.
- Market Entry Strategies: Guiding decisions on entry modes, partnerships, or acquisitions.
- Localization: Tailoring products, services, and marketing to suit local market preferences.
9.3 Product Development and Innovation
Market reports provide valuable information for product development and innovation efforts:
- Identifying Market Gaps: Reports highlight unmet needs and gaps in the market that can be addressed through new products or services.
- Market Demand: Understanding market demand and preferences informs product features and design.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Analyzing competitor offerings aids in product differentiation.
9.4 Marketing and Branding
Market reports play a crucial role in marketing and branding strategies:
- Targeted Marketing: Reports inform the creation of targeted marketing campaigns aimed at specific market segments.
- Messaging: Insights from reports help tailor messaging and positioning to resonate with target audiences.
- Brand Strategy: Reports aid in shaping brand strategies based on market perceptions and trends.
9.5 Investment and Funding
Investors and financial institutions rely on market reports to make informed investment decisions:
- Due Diligence: Investors use reports to conduct due diligence on potential investment opportunities.
- Risk Assessment: Reports help assess investment risks and opportunities in different sectors and markets.
- Valuation: Reports provide data for valuing businesses and assets accurately.
9.6 Policy and Government Decision-Making
Government agencies and policymakers use market reports to inform policies and regulations:
- Economic Planning: Reports help governments plan economic policies and initiatives based on market conditions.
- Consumer Protection: Insights into market behavior inform consumer protection regulations.
- Industry Regulation: Regulators use reports to monitor industry compliance and identify areas requiring regulation.
9.7 Academic Research and Education
Market reports are valuable resources for academic research and education:
- Data Sources: Reports provide data and statistics for academic research and coursework.
- Case Studies: Real-world case studies based on market reports enrich educational materials.
- Market Dynamics: Reports offer insights into market dynamics for academic analysis.
9.8 Nonprofit and NGO Activities
Nonprofit organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) use market reports for:
- Needs Assessment: Reports help assess the needs of target populations and communities.
- Fundraising: Data from reports supports grant applications and fundraising efforts.
- Impact Assessment: NGOs use market reports to measure the impact of their programs and initiatives.
9.9 Environmental and Sustainability Initiatives
Market reports play a role in environmental and sustainability initiatives:
- Market Trends: Reports highlight sustainability trends and consumer preferences.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Businesses use reports to assess the environmental impact of their supply chains.
- Regulatory Compliance: Reports help organizations stay compliant with environmental regulations.
9.10 International Trade and Export
Market reports assist businesses and governments in international trade and export activities:
- Export Planning: Reports inform export strategies, including market selection and product adaptation.
- Market Access: Reports help businesses navigate trade barriers and regulatory requirements in foreign markets.
- Trade Negotiations: Governments use reports to support trade negotiations and agreements.
Market reports are versatile tools that empower organizations and individuals across various sectors to make informed decisions, drive growth, and contribute to economic, social, and environmental goals. Their practical applications are wide-ranging and impactful, making them an essential component of modern business and decision-making processes.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Market Reports
In the dynamic world of business and decision-making, market reports are indispensable tools that empower individuals and organizations to navigate the complexities of markets, industries, and economies. Through this comprehensive guide, we have explored the art of market reports, from the fundamentals to advanced strategies. As we conclude our journey through this knowledge-rich resource, let us reflect on the key takeaways and the importance of mastering the craft of market reports.
The Power of Informed Decision-Making
Market reports are not just documents; they are instruments of informed decision-making. Whether you are a business leader shaping corporate strategy, an investor assessing opportunities, a policymaker crafting regulations, or an academic exploring market dynamics, market reports provide the critical insights needed to make sound choices.
The Art and Science of Market Research
Market reports are both an art and a science. They require meticulous planning, rigorous research methodologies, and data-driven analysis. Yet, they also demand creativity in storytelling, clarity in communication, and the ability to transform raw data into actionable insights that resonate with diverse audiences.
The Role of Market Reports Across Industries
Market reports have universal relevance, transcending industry boundaries. From finance to healthcare, technology to agriculture, and beyond, market reports play a pivotal role in strategy development, risk mitigation, and sustainable growth.
Ethical Conduct in Market Research
Ethical considerations are at the heart of responsible market research and reporting. Respecting privacy, citing sources, avoiding bias, and adhering to legal and regulatory frameworks are non-negotiable principles that safeguard the integrity of market reports.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
In the fast-paced landscape of markets and industries, the journey of mastering market reports is ongoing. Embrace a commitment to continuous learning, staying updated on emerging trends, technologies, and ethical guidelines. Seek opportunities to refine your skills and expand your knowledge.
The Collaborative Nature of Market Reporting
Market reporting thrives on collaboration. It involves multidisciplinary teams, from researchers and analysts to designers and communicators. It also requires engagement with stakeholders, clients, and consumers to ensure that reports meet their needs.
Empowering Decision-Makers
Ultimately, market reports are instruments of empowerment. They provide decision-makers with the knowledge and insights needed to chart a course toward success, navigate challenges, and seize opportunities. In an era of information overload, market reports cut through the noise to deliver actionable intelligence.
As we conclude our exploration of market reports, remember that you are equipped with the skills and knowledge to harness the power of these invaluable tools. Whether you are producing market reports, using them to inform decisions, or simply seeking to expand your understanding, your journey in mastering the art of market reports has the potential to drive innovation, fuel growth, and shape the future.
The world of markets and industries is ever-evolving, and so too is the art of market reporting. Embrace this evolution with enthusiasm, integrity, and a commitment to excellence, for it is through the mastery of market reports that we unlock the insights that shape the world around us.
Appendices: Additional Resources and Templates
In the appendices of this comprehensive guide on market reports, we provide additional resources and templates to assist you in your market research and reporting endeavors. These resources are designed to enhance your understanding and streamline your reporting process.
A.1 Market Report Template
Use this market report template as a starting point for creating your own market reports. The template includes sections for the executive summary, introduction, methodology, findings, recommendations, and more. Customize it to fit your specific research and reporting needs.
A.2 Data Sources and References
When conducting market research, it's essential to rely on credible data sources and references. This appendix provides a list of reputable sources for market data, reports, and academic research across various industries.
A.3 Market Research Tools and Software
Explore a selection of market research tools and software that can aid in data collection, analysis, and visualization. These tools can help streamline your research process and enhance the quality of your market reports.
A.4 Sample Case Studies
Sample case studies illustrate how market reports have been used in real-world scenarios. These case studies provide insights into the practical applications of market research and reporting across different industries.
A.5 Ethical Guidelines for Market Research
Ethical considerations are paramount in market research. This appendix outlines ethical guidelines and best practices for conducting research that respects the rights and privacy of individuals and organizations.
A.6 Glossary of Terms
A comprehensive glossary of key terms and concepts related to market research and reporting. Use this resource to clarify any terminology encountered during your research and reporting activities.
A.7 Further Reading and Resources
This section provides a list of recommended books, articles, websites, and organizations dedicated to market research and reporting. Explore these resources to deepen your knowledge and stay updated on industry trends.
A.8 Feedback and Contact Information
We value your feedback and are open to answering any questions or providing additional assistance. Contact information is provided for inquiries, suggestions, or further assistance related to market research and reporting.
These appendices serve as valuable companions to the core chapters of this guide, providing practical tools, references, and guidance to support your market research and reporting endeavors. Whether you're a business professional, researcher, student, or entrepreneur, these resources are designed to enhance your capabilities in the field of market analysis and reporting.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.