Database and Business Intelligence
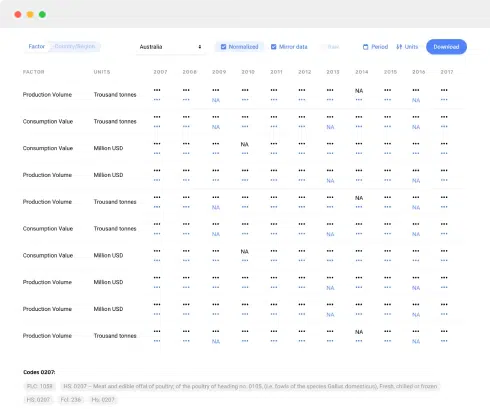
A database is a structured collection of data that is stored and managed in a systematic way. It is designed to efficiently store, retrieve, and manipulate large quantities of information. Databases are an essential component of any business as they enable efficient data management and provide a central repository for storing critical business information.
A database typically consists of tables, which are organized into rows and columns. Each row represents a record or a data instance, while each column represents a specific attribute or data field. The logical structure of a database is known as the schema, which defines the tables, relationships between tables, and constraints on the data.
Relational databases are the most common type of database used in business applications. They allow data to be organized into tables and define relationships between tables using keys. This enables users to retrieve and manipulate data using structured query language (SQL). Relational databases provide a secure and reliable way to store data, and they offer various features such as data integrity, concurrency control, and backup and recovery mechanisms.
Business intelligence (BI) refers to the technologies, applications, and practices for collecting, integrating, analyzing, and presenting business information. It involves turning raw data into meaningful insights to support strategic decision-making and enhance overall business performance.
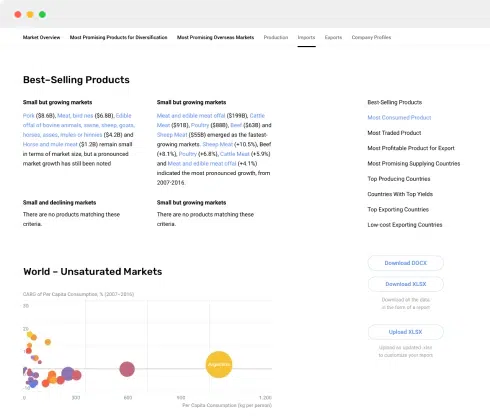
BI utilizes various tools and techniques to extract, transform, and load data from multiple sources such as databases, data warehouses, and external systems. These sources may contain structured or unstructured data from different business operations. By consolidating data from various sources, BI systems provide a holistic view of the organization's information.
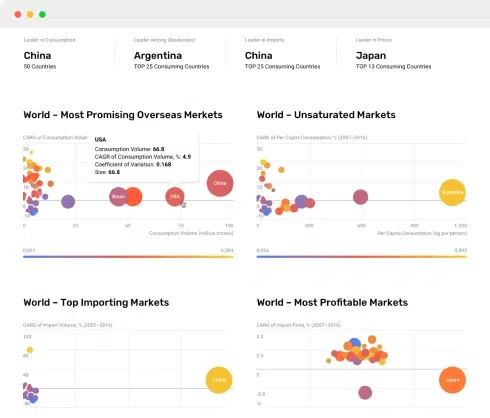
BI incorporates data analytics, data visualization, and reporting capabilities to enable users to explore, analyze, and understand data trends, patterns, and relationships. It allows organizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify opportunities, and make data-driven decisions.
BI offers several benefits to businesses, including improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making, greater operational insights, and competitive advantage. By providing real-time dashboards and reports, BI enables executives and managers to monitor business performance and identify areas for improvement or intervention.
Overall, databases and business intelligence play crucial roles in managing and leveraging data for business success. Databases provide a robust foundation for storing and organizing data, while BI empowers organizations to extract actionable insights from that data, driving informed decision-making and improving business outcomes.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.
Nothing found. Please try again.