Indonesia - Sugar Crops - Market Analysis, Forecast, Size, Trends and Insights
Get instant access to more than 2 million reports, dashboards, and datasets on the IndexBox Platform.
View PricingJoin Us at HANNOVER MESSE 2024
Don’t miss your chance to connect with us directly. Schedule a personal meeting to dive deeper into how solutions.
Hall 002, Stand C10. 22 - 26 April 2024 | Hannover, Germany

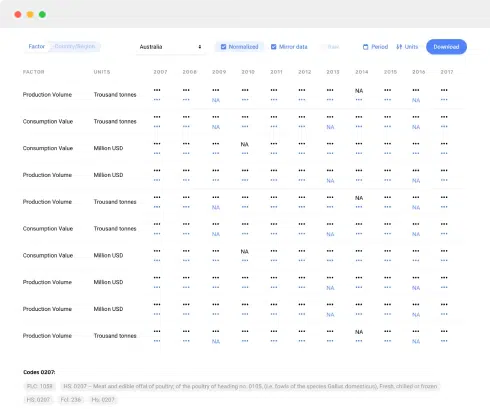
Source: IndexBox Platform
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the sugar crop market in Indonesia. Within it, you will discover the latest data on market trends and opportunities by country, consumption, production and price developments, as well as the global trade (imports and exports). The forecast exhibits the market prospects through 2030.
Product coverage:
- FCL 161 - Sugar crops nes
Country coverage:
- Indonesia
Data coverage:
- Market volume and value
- Per Capita consumption
- Forecast of the market dynamics in the medium term
- Trade (exports and imports) in Indonesia
- Export and import prices
- Market trends, drivers and restraints
- Key market players and their profiles
Reasons to buy this report:
- Take advantage of the latest data
- Find deeper insights into current market developments
- Discover vital success factors affecting the market
This report is designed for manufacturers, distributors, importers, and wholesalers, as well as for investors, consultants and advisors.
In this report, you can find information that helps you to make informed decisions on the following issues:
- How to diversify your business and benefit from new market opportunities
- How to load your idle production capacity
- How to boost your sales on overseas markets
- How to increase your profit margins
- How to make your supply chain more sustainable
- How to reduce your production and supply chain costs
- How to outsource production to other countries
- How to prepare your business for global expansion
While doing this research, we combine the accumulated expertise of our analysts and the capabilities of artificial intelligence. The AI-based platform, developed by our data scientists, constitutes the key working tool for business analysts, empowering them to discover deep insights and ideas from the marketing data.
-
1. INTRODUCTION
Making Data-Driven Decisions to Grow Your Business
- REPORT DESCRIPTION
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND AI PLATFORM
- DATA-DRIVEN DECISIONS FOR YOUR BUSINESS
- GLOSSARY AND SPECIFIC TERMS
-
2. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
A Quick Overview of Market Performance
- KEY FINDINGS
- MARKET TRENDS This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO
-
3. MARKET OVERVIEW
Understanding the Current State of The Market and Its Prospects
- MARKET SIZE
- MARKET STRUCTURE
- TRADE BALANCE
- PER CAPITA CONSUMPTION
- MARKET FORECAST TO 2030
-
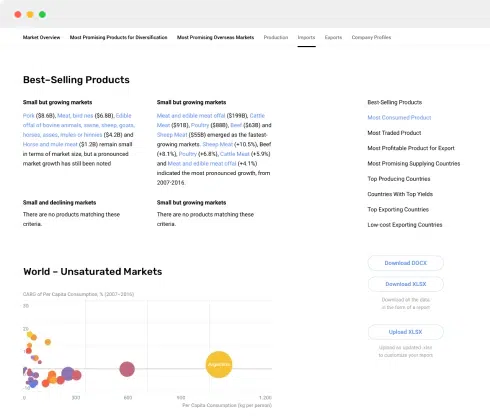
4. MOST PROMISING PRODUCT
Finding New Products to Diversify Your Business
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP PRODUCTS TO DIVERSIFY YOUR BUSINESS
- BEST-SELLING PRODUCTS
- MOST CONSUMED PRODUCT
- MOST TRADED PRODUCT
- MOST PROFITABLE PRODUCT FOR EXPORT
-
5. MOST PROMISING SUPPLYING COUNTRIES
Choosing the Best Countries to Establish Your Sustainable Supply Chain
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP COUNTRIES TO SOURCE YOUR PRODUCT
- TOP PRODUCING COUNTRIES
- COUNTRIES WITH TOP YIELDS
- TOP EXPORTING COUNTRIES
- LOW-COST EXPORTING COUNTRIES
-
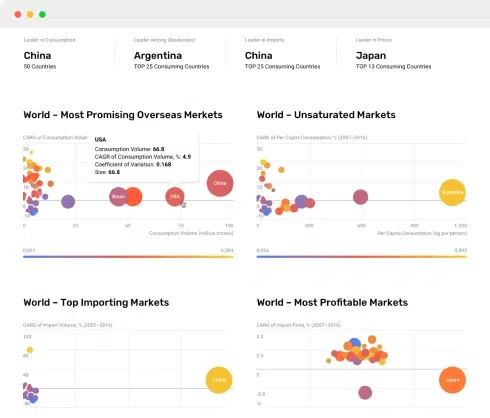
6. MOST PROMISING OVERSEAS MARKETS
Choosing the Best Countries to Boost Your Exports
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP OVERSEAS MARKETS FOR EXPORTING YOUR PRODUCT
- TOP CONSUMING MARKETS
- UNSATURATED MARKETS
- TOP IMPORTING MARKETS
- MOST PROFITABLE MARKETS
7. PRODUCTION
The Latest Trends and Insights into The Industry
- PRODUCTION, HARVESTED AREA AND YIELD
8. IMPORTS
The Largest Import Supplying Countries
- IMPORTS FROM 2012–2023
- IMPORTS BY COUNTRY
- IMPORT PRICES BY COUNTRY
9. EXPORTS
The Largest Destinations for Exports
- EXPORTS FROM 2012–2023
- EXPORTS BY COUNTRY
- EXPORT PRICES BY COUNTRY
-
10. PROFILES OF MAJOR PRODUCERS
The Largest Producers on The Market and Their Profiles
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO -
LIST OF TABLES
- Key Findings In 2023
- Market Volume, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Market Value, 2012–2023
- Per Capita Consumption In 2012-2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Import Prices, By Country Of Origin, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Export Prices, By Country Of Destination, 2012–2023
-
LIST OF FIGURES
- Market Volume, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Market Value, 2012–2023
- Market Structure – Domestic Supply vs. Imports, In Physical Terms, 2012-2023
- Market Structure – Domestic Supply vs. Imports, In Value Terms, 2012-2023
- Trade Balance, In Physical Terms, 2012-2023
- Trade Balance, In Value Terms, 2012-2023
- Per Capita Consumption, 2012-2023
- Market Volume Forecast to 2030
- Market Value Forecast to 2030
- Products: Market Size And Growth, By Type
- Products: Average Per Capita Consumption, By Type
- Products: Exports And Growth, By Type
- Products: Export Prices And Growth, By Type
- Production Volume And Growth
- Yield And Growth
- Exports And Growth
- Export Prices And Growth
- Market Size And Growth
- Per Capita Consumption
- Imports And Growth
- Import Prices
- Production, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Production, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Area Harvested, 2012–2023
- Yield, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Import Prices, By Country Of Origin, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Export Prices, By Country Of Destination, 2012–2023
Recommended reports
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global sugar crop market.
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the sugar crop market in the EU.
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the sugar crop market in Asia.
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the sugar crop market in the U.S..
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the sugar crop market in China.