World - Biodiesel - Market Analysis, Forecast, Size, Trends And Insights
Get instant access to more than 2 million reports, dashboards, and datasets on the IndexBox Platform.
View PricingBiofuel From Agricultural Waste
Biofuels are renewable fuels that are derived from natural organic matter such as agricultural waste. Agricultural waste contains a significant amount of biomass that can be used as a raw material for the production of biofuels. The process of converting agricultural waste to biofuels is known as bioconversion, which involves the use of microorganisms or enzymes to break down the complex organic matter into simpler forms that can be used to produce biofuels.
Biofuels from agricultural waste have been gaining increasing attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. These fuels offer a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels as they emit fewer greenhouse gases and are produced from renewable sources. Additionally, the production of biofuels from agricultural waste can also create a new source of revenue for farmers and rural communities.
The most common types of agricultural waste used for biofuel production include crop residues, such as corn stover, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse, as well as animal manure and food waste. These materials are rich in cellulose and hemicellulose, which can be broken down into simple sugars through a process known as hydrolysis. The resulting sugar solution can then be fermented to produce biofuels such as ethanol, butanol, and biogas.
Ethanol is the most widely used biofuel and is primarily produced by the fermentation of sugar or starch-derived from corn or sugarcane. However, with the limited availability of land and freshwater resources, the use of agricultural waste as a feedstock for ethanol production is gaining momentum. The use of agricultural waste can also reduce the competition between food and fuel production, which has been a major issue with the traditional biofuel production using food crops.
Biogas is another biofuel that can be produced from agricultural waste, specifically from animal manure. Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced through anaerobic digestion, a process that involves the breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. The resulting gas contains methane, which can be used as a fuel for cooking and heating.
In conclusion, biofuels derived from agricultural waste are a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels. These fuels offer a sustainable and renewable source of energy that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. The production of biofuels from agricultural waste can also provide new sources of revenue for farmers and rural communities while reducing the competition between food and fuel production. With ongoing research and development, the commercial viability and capacity of biofuels from agricultural waste can be further enhanced, opening up opportunities for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global biodiesel market. Within it, you will discover the latest data on market trends and opportunities by country, consumption, production and price developments, as well as the global trade (imports and exports). The forecast exhibits the market prospects through 2030.
Product coverage:
- Prodcom 20595997 - Biofuels (diesel substitute)
Country coverage:
Worldwide - the report contains statistical data for 200 countries and includes detailed profiles of the 50 largest consuming countries:
- USA
- China
- Japan
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Brazil
- Italy
- Russian Federation
- India
- Canada
- Australia
- Republic of Korea
- Spain
- Mexico
- Indonesia
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Saudi Arabia
- Switzerland
- Sweden
- Nigeria
- Poland
- Belgium
- Argentina
- Norway
- Austria
- Thailand
- United Arab Emirates
- Colombia
- Denmark
- South Africa
- Malaysia
- Israel
- Singapore
- Egypt
- Philippines
- Finland
- Chile
- Ireland
- Pakistan
- Greece
- Portugal
- Kazakhstan
- Algeria
- Czech Republic
- Qatar
- Peru
- Romania
- Vietnam
+ the largest producing countries
Data coverage:
- Global market volume and value
- Per Capita consumption
- Forecast of the market dynamics in the medium term
- Global production, split by region and country
- Global trade (exports and imports)
- Export and import prices
- Market trends, drivers and restraints
- Key market players and their profiles
Company coverage:
Reasons to buy this report:
- Take advantage of the latest data
- Find deeper insights into current market developments
- Discover vital success factors affecting the market
This report is designed for manufacturers, distributors, importers, and wholesalers, as well as for investors, consultants and advisors.
In this report, you can find information that helps you to make informed decisions on the following issues:
- How to diversify your business and benefit from new market opportunities
- How to load your idle production capacity
- How to boost your sales on overseas markets
- How to increase your profit margins
- How to make your supply chain more sustainable
- How to reduce your production and supply chain costs
- How to outsource production to other countries
- How to prepare your business for global expansion
While doing this research, we combine the accumulated expertise of our analysts and the capabilities of artificial intelligence. The AI-based platform, developed by our data scientists, constitutes the key working tool for business analysts, empowering them to discover deep insights and ideas from the marketing data.
-
1. INTRODUCTION
Making Data-Driven Decisions to Grow Your Business
- REPORT DESCRIPTION
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND AI PLATFORM
- DATA-DRIVEN DECISIONS FOR YOUR BUSINESS
- GLOSSARY AND SPECIFIC TERMS
-
2. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
A Quick Overview of Market Performance
- KEY FINDINGS
- MARKET TRENDS This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO
-
3. MARKET OVERVIEW
Understanding the Current State of The Market and Its Prospects
- MARKET SIZE
- CONSUMPTION BY COUNTRY
- MARKET FORECAST TO 2030
-
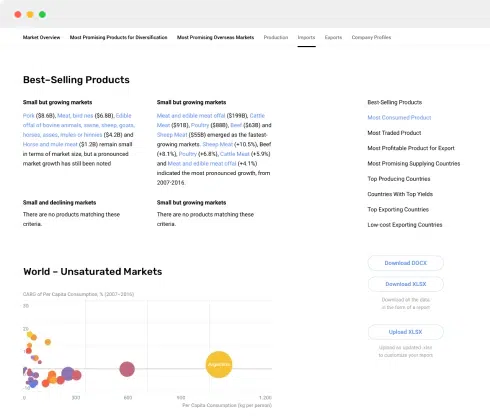
4. MOST PROMISING PRODUCT
Finding New Products to Diversify Your Business
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP PRODUCTS TO DIVERSIFY YOUR BUSINESS
- BEST-SELLING PRODUCTS
- MOST CONSUMED PRODUCT
- MOST TRADED PRODUCT
- MOST PROFITABLE PRODUCT FOR EXPORT
-
5. MOST PROMISING SUPPLYING COUNTRIES
Choosing the Best Countries to Establish Your Sustainable Supply Chain
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP COUNTRIES TO SOURCE YOUR PRODUCT
- TOP PRODUCING COUNTRIES
- TOP EXPORTING COUNTRIES
- LOW-COST EXPORTING COUNTRIES
-
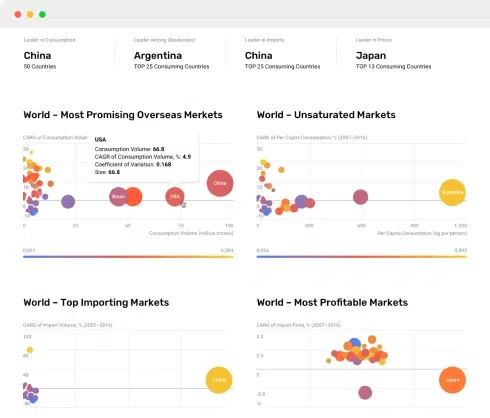
6. MOST PROMISING OVERSEAS MARKETS
Choosing the Best Countries to Boost Your Exports
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- TOP OVERSEAS MARKETS FOR EXPORTING YOUR PRODUCT
- TOP CONSUMING MARKETS
- UNSATURATED MARKETS
- TOP IMPORTING MARKETS
- MOST PROFITABLE MARKETS
7. GLOBAL PRODUCTION
The Latest Trends and Insights into The Industry
- PRODUCTION VOLUME AND VALUE
- PRODUCTION BY COUNTRY
8. GLOBAL IMPORTS
The Largest Importers on The Market and How They Succeed
- IMPORTS FROM 2012–2023
- IMPORTS BY COUNTRY
- IMPORT PRICES BY COUNTRY
9. GLOBAL EXPORTS
The Largest Exporters on The Market and How They Succeed
- EXPORTS FROM 2012–2023
- EXPORTS BY COUNTRY
- EXPORT PRICES BY COUNTRY
-
10. PROFILES OF MAJOR PRODUCERS
The Largest Producers on The Market and Their Profiles
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO -
11. COUNTRY PROFILES
The Largest Markets And Their Profiles
This Chapter is Available Only for the Professional Edition PRO- United States
- China
- Japan
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Brazil
- Italy
- Russian Federation
- India
- Canada
- Australia
- Republic of Korea
- Spain
- Mexico
- Indonesia
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Saudi Arabia
- Switzerland
- Sweden
- Nigeria
- Poland
- Belgium
- Argentina
- Norway
- Austria
- Thailand
- United Arab Emirates
- Colombia
- Denmark
- South Africa
- Malaysia
- Israel
- Singapore
- Egypt
- Philippines
- Finland
- Chile
- Ireland
- Pakistan
- Greece
- Portugal
- Kazakhstan
- Algeria
- Czech Republic
- Qatar
- Peru
- Romania
- Vietnam
-
LIST OF TABLES
- Key Findings In 2023
- Market Volume, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Market Value, 2012–2023
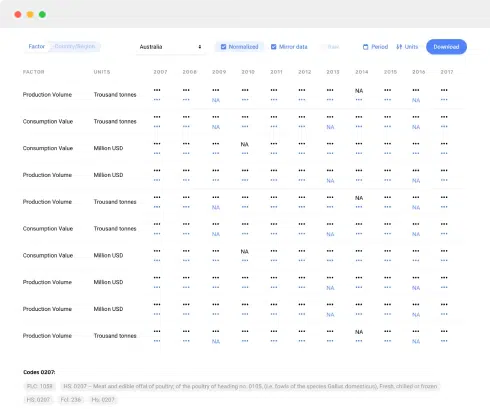
- Per Capita Consumption, By Country, 2018–2023
- Production, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Import Prices, By Country Of Destination, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Export Prices, By Country Of Origin, 2012–2023
-
LIST OF FIGURES
- Market Volume, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Market Value, 2012–2023
- Consumption, By Country, 2023
- Market Volume Forecast to 2030
- Market Value Forecast to 2030
- Products: Market Size And Growth, By Type
- Products: Average Per Capita Consumption, By Type
- Products: Exports And Growth, By Type
- Products: Export Prices And Growth, By Type
- Production Volume And Growth
- Exports And Growth
- Export Prices And Growth
- Market Size And Growth
- Per Capita Consumption
- Imports And Growth
- Import Prices
- Production, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Production, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Production, By Country, 2023
- Production, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2023
- Imports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Imports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Import Prices, By Country, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2023
- Exports, In Physical Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Exports, In Value Terms, By Country, 2012–2023
- Export Prices, 2012–2023
Explore the top import markets for biodiesel globally and understand the key statistics and trends. Discover the countries leading the biodiesel import market and their import values as per the IndexBox market intelligence platform.
Discover the top import markets for biodiesel and how these countries are driving the growth of the industry. Learn why the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Germany, and Spain are leading the way in biodiesel imports.
This year, Belgium is overtaking Germany to emerge as the second-largest biodiesel exporter in the world. From January to July 2021, Belgium supplied biodiesel worth $2.1B abroad, while Germany’s exports were estimated at $1.8B. The Netherlands keeps the leading position with a biodiesel export value of $4.2B. In 2020, Germany ($2.3B) followed the Netherlands ($4.6B) in global export ranking, while Belgium ($1.5B) took third place. The average biodiesel export price grew by +11% y-o-y to $979 per ton in 2020.
Neither the pandemic nor the low oil prices succeeded in slowing the growth of the global biodiesel market. As economies worldwide start to recover from the Covid crisis, and environmental concerns increase, the demand is set to remain robust in 2021.